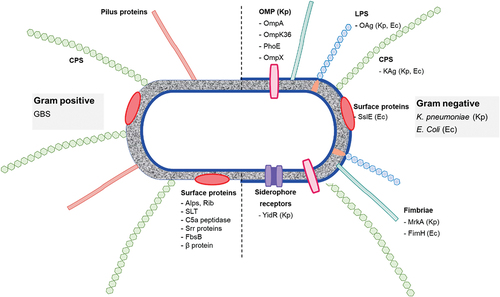
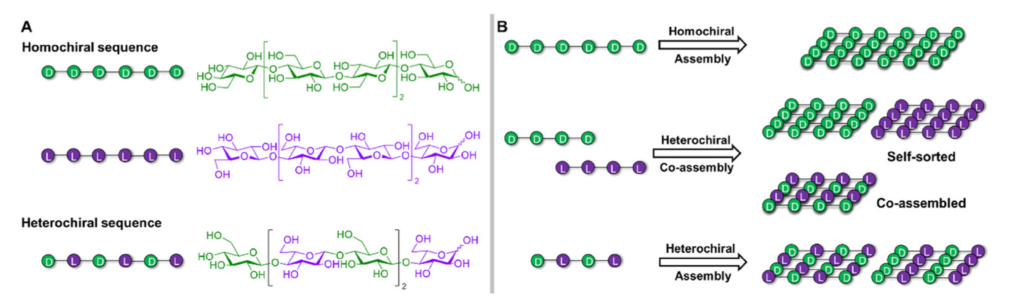
Viral pandemics remain a persistent threat to global health and economic stability. Despite advancements in medicine, a lack of broad-spectrum antivirals (BSAs) hinders swift responses to new viral outbreaks. This challenge mainly stems from the absence of universal drug targets across different viral families and the high diversity of viral proteins. In our research, we tested 57 synthetic carbohydrate receptors (SCRs) for antiviral activity in cell culture, using pseudotyped virus particles (PVPs) from six high-risk viruses spanning three families: Paramyxoviridae, Filoviridae, and Coronaviridae. Four SCRs successfully inhibited all tested PVPs, and their effectiveness was validated against live viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, EBOV, MARV, NiV, and HeV.
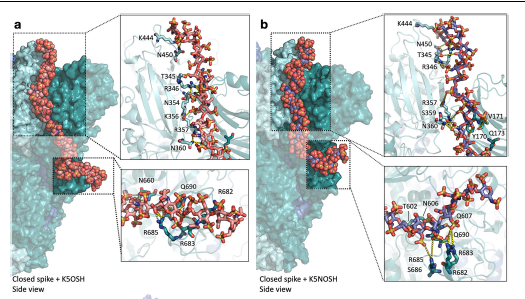
Notably, SCR005 and SCR007, which showed minimal toxicity, greatly decreased SARS-CoV-2 infection in a severe animal model with just one dose. Mechanistic studies indicate that SCRs attach to viral envelope N-glycans, preventing viral attachment and fusion. These findings highlight conserved viral N-glycans as promising BSA targets and position SCRs as potential prophylactic agents against enveloped viruses with pandemic potential.
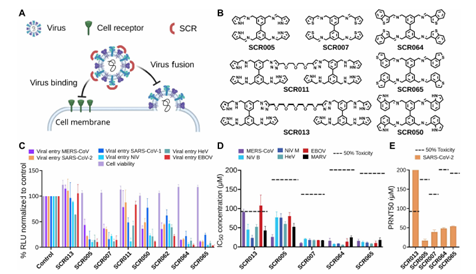
analysis of luciferase activity, which was then quantified in comparison to control cells treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (based on three independent studies). (D and E) IC₅₀ and CC ₅₀ values were determined using GraphPad Prism 10 by fitting dose-response curves with a four-parameter logistic (4PL) nonlinear regression model in Vero cells. This was accomplished using the PRNT test and IFA with spike protein immunostaining in cells that received pretreatment (SCR005, SCR007, SCR0064, SCR0065, and SCR0013, compared to 0.1% DMSO, n ≥ 3). The intermittent line indicates 50% toxicity.