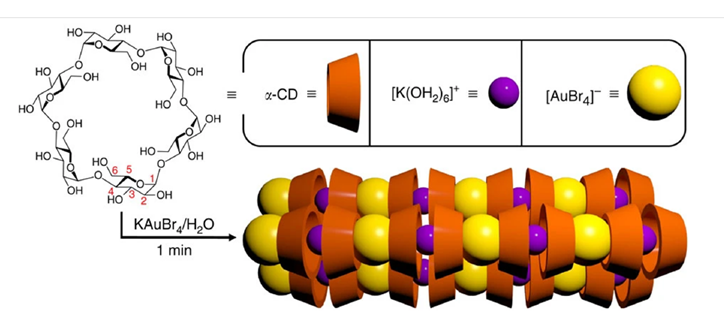
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are known for their ability to form supramolecular interactions with a wide range of guest molecules. In this review, the focus is given on the inclusion of complex aurate ions such as tetrabromoaurate, dicyanoaurate, and a few other tetrahaloaurates. The review describes the properties of self-assembly of cyclodextrins with these ions, with a highlight to α-CD and, more recently, β-CD, requiring the use of a co-former/precipitating agent. Practical applications of this ability include the selective isolation of gold from a variety of sources, ranging from gold-rich mining ores and tailings/mining wastes to gold-bearing metal scraps obtained from discarded electronic devices. Moreover, it describes the development of a method based on the spontaneous complex formation between α-CD and tetrabromoaurate, as well as its current status of use in a few mining sites in the United States.