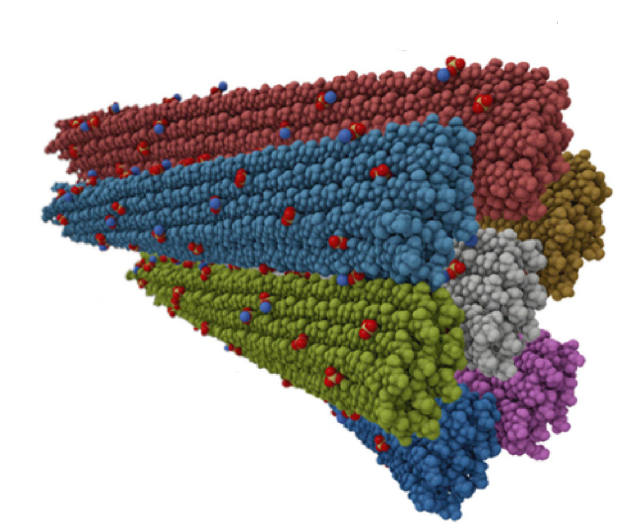
The complexity of plant cell walls at different hierarchical levels still hinders the detailed understanding of biosynthetic pathways, impedes processing in industry, and ultimately limits the applicability of cellulosic materials. While there are many challenges to readily accessing these hierarchies at (sub-)angstrom resolution, the development of advanced computational methods has the potential to unravel essential questions in this field. Here, the authors discuss the contributions of molecular dynamics simulations in advancing the understanding of the physicochemical properties of natural fibres. The aim is to provide a comprehensive overview of the advances and insights gained from molecular dynamics simulations in carbohydrate polymer research. The review is a critical reference for researchers wishing to perform atomistic simulations of plant cell wall constituents. Its importance extends beyond molecular modelling and chemistry, providing a pathway to a deeper understanding of plant cell walls’ chemistry, interactions and behaviour. By delving into these fundamental aspects, the review offers invaluable insights into future avenues of research. Researchers within the molecular modelling and carbohydrate communities can benefit greatly from this resource, enabling them to make significant progress in unravelling the intricacies of plant cell wall dynamics.