Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative disease affecting cartilage, synovium, and bone, and it is a major cause of pain and disability. Intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid (HA) derivatives, also known as visco-supplementation (VS), is a common treatment for the symptomatic management of knee OA. Despite its widespread use, the magnitude of the clinical benefit of VS remains controversial, with conflicting results due to methodological differences and possible differences in efficacy between products related to remanence and rheological properties.
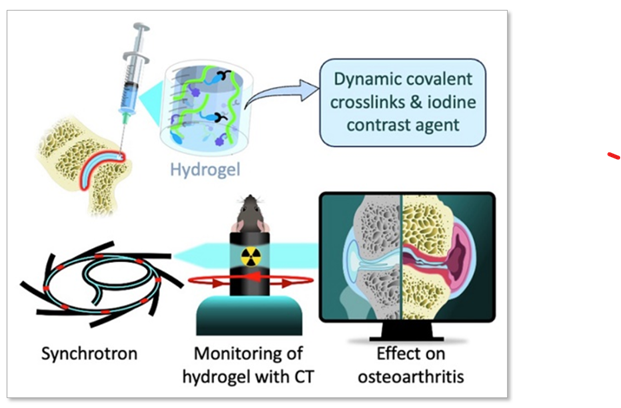
To create an effective HA-based treatment, an injectable self-healing HA hydrogel with long-persistent radiopacity is formed by tethering a clinical iodine contrast agent to HA. The labeling conditions are tuned to obtain sufficient X-ray signal without altering the hydrogel’s biocompatibility, rheological, and injectability properties.
The iodine labeling enables monitoring not only the delivery of the hydrogel but also its retention in mouse knees up to 5 weeks post-administration using synchrotron K-edge subtraction-computed tomography. The authors further demonstrated that the unique properties of this hydrogel enable the creation of an in vivo transient HA network that attenuates OA progression in a mouse model of OA. Moreover, our data showed that the rate of HA-I disappearance appears to predict treatment response, likely because a rapid elimination serves as an indirect indicator of in situ inflammation.
Collectively, these results show that the radiopaque HA-I hydrogel holds significant promise for improving patient management in the treatment of OA before clinical symptoms worsen. Over time, its capacity for in vivo tracking allows personalized treatment schedules based on observed retention and therapeutic effect. As a result, this theranostic hydrogel emerges as a strong candidate for precision medicine in OA.