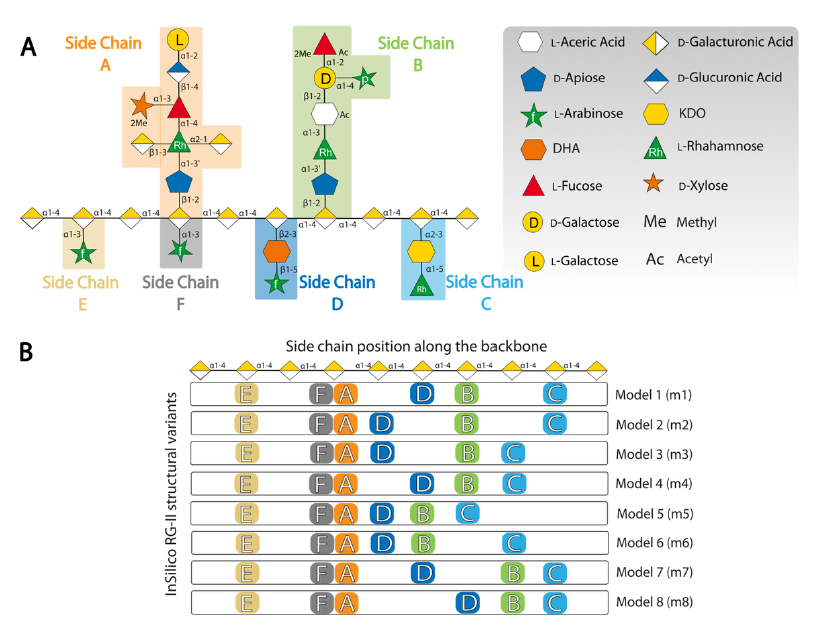
Rhamnogalacturonan-II (RG-II) is the most complex polysaccharide known in Nature and plays an indispensable role in the growth and development of all vascular plants. RG-II is characterized by 12 different monosaccharides connected via a multiplicity of glycosidic linkages. The constituent monosaccharide units are arranged into six different sidechains along a polygalacturonic-acid backbone connected by α-1-4 linkages. While the side-chain constituent residues are known, their relative locations along the backbone have not yet been resolved. In this study, we grow, isolate, and characterize RG-II from celery cells and use solution-based NMR in concert with molecular dynamics simulations on 8 distinct structural variants to identify and propose the first atomistic 3-D structure of RG-II that best represents the experimental NOE data. The authors parameterize the forcefields for unique sugars and linkages and employ replica-exchange molecular dynamics to sample the complex conformational landscape for RG-II adequately. The present biophysical approach provides a foundation for establishing sequence-structure relationships for RG-II and enabling the tools and metrics to relate its structure to its function.