Glycans attached to glycoproteins can contribute to stability, mediate interactions with other proteins, and initiate signal transduction. Glycan conformation, critical to these
processes is highly variable and often depicted as sampling a multitude of conformers. These conformers can be generated by molecular dynamics simulations and more inclusively by accelerated molecular dynamics, as well as other extended sampling methods. However, experimental assessments of various conformers’ contributions to a native ensemble are rare. The authors use long-range pseudo-contact shifts (PCSs) of NMR resonances from an isotopically labeled glycoprotein to identify preferred conformations of its glycans.
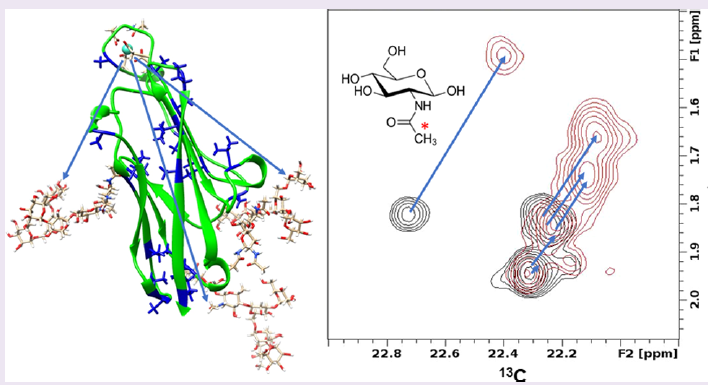
This study used the N-terminal domain from human Carcinoembryonic Antigen Cell Adhesion Molecule 1, hCEACAM1-Ig1, as the model glycoprotein. It has been engineered to include a lanthanide-ion-binding loop that generates PCSs and a homogeneous set of three 13C-labeled N-glycans. Analysis of the PCSs indicates that preferred glycan conformers have extensive contacts with the protein surface. Factors leading to this preference appear to include interactions between N-acetyl methyls of GlcNAc residues and hydrophobic surface pockets on the protein surface.