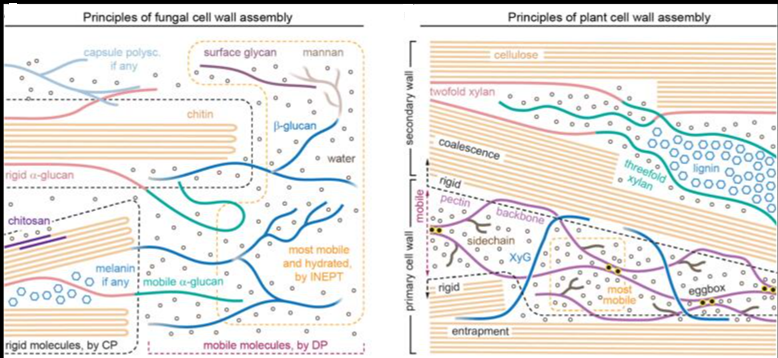
Recent waves of COVID-19 correlate with the emergence of the Delta and the Omicron variant. The authors report that the Spike trimer acts as a highly dynamic molecular calliper, forming up to three tight bonds through its RBDs with ACE2 expressed on the cell surface. The Spike of both Delta and Omicron (B.1.1.529).
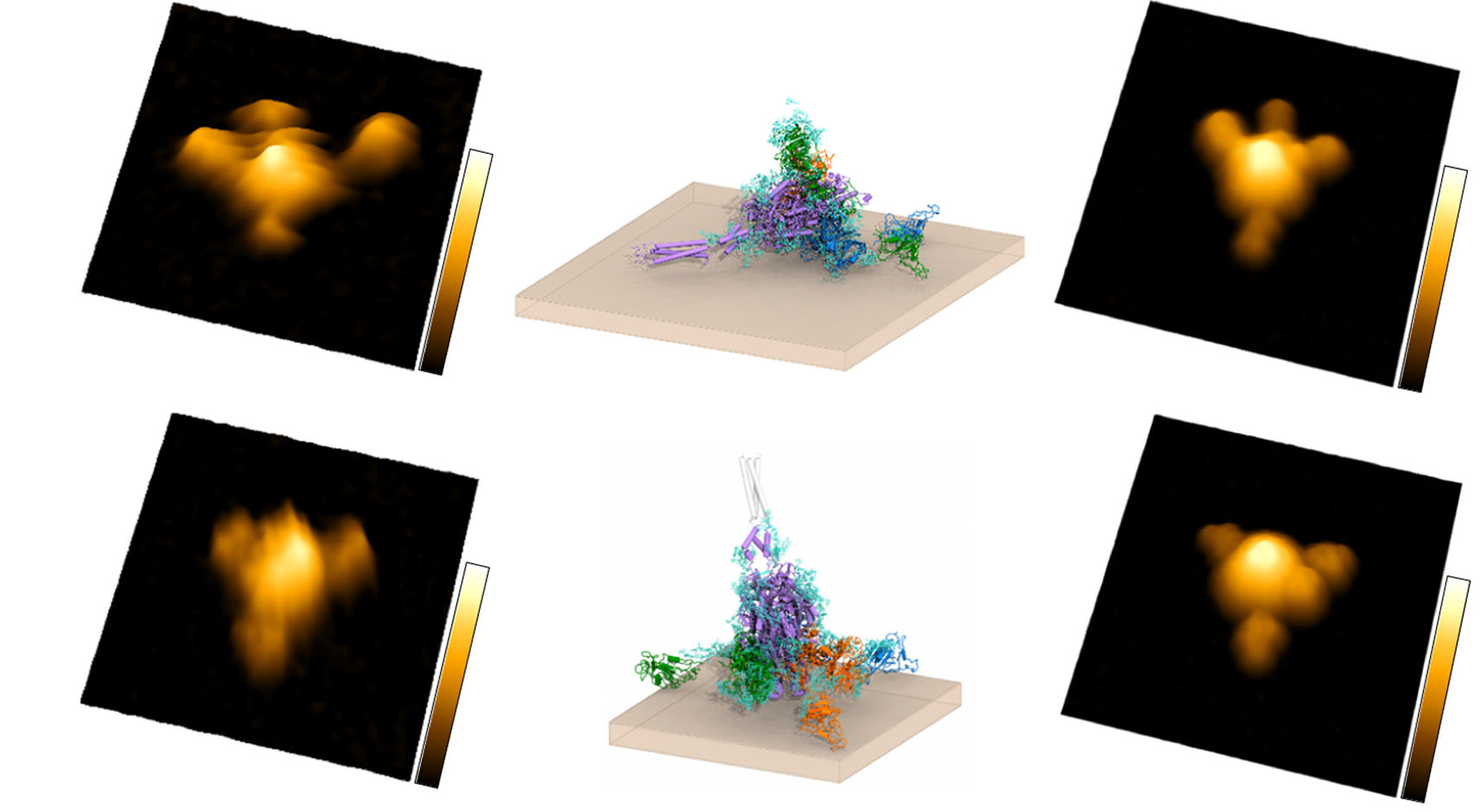
Variant enhances and markedly prolongs viral attachment to the host cell receptor ACE2 instead of the early Wuhan-1 isolate. Delta Spike shows rapid binding of all three Spike RBDs to three different ACE2 molecules with considerably increased bond lifetime compared to the reference strain, thereby significantly amplifying avidity. Intriguingly, Omicron (B.1.1.529) Spike displays less multivalent bindings to ACE2 molecules, yet with a ten times longer bond lifetime than Delta. Delta and Omicron (B.1.1.529) Spike variants enhance and prolong viral attachment to the host, which likely not only increases the rate of viral uptake but also enhances the resistance of the variants against host-cell detachment by shear forces such as airflow, mucus or blood flow. The authors uncover distinct binding mechanisms and strategies at single-molecule resolution employed by circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants to enhance infectivity and viral transmission.