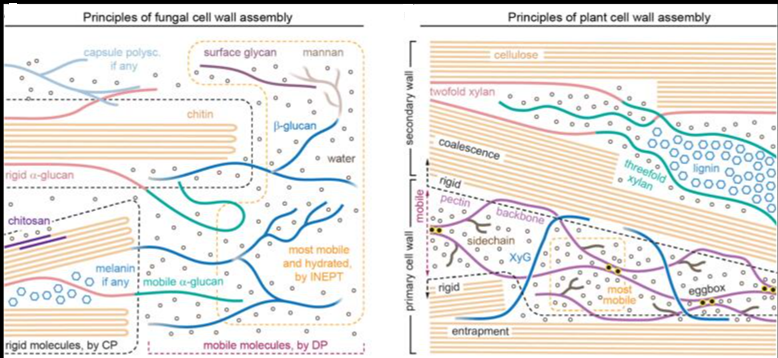
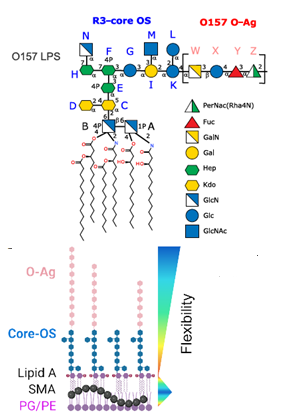
Chitin is the second most abundant natural polymer in the world after cellulose, mainly derived from the food waste of shrimp and crabs. Chitosan is the most important derivative of chitin. Thanks to their biodegradability, non-toxicity, biocompatibility, bioactivity, and versatile chemical and physical properties, chitin and chitosan derivatives are used in a wide variety of applications, including water treatment, cosmetics and toiletries, food and beverages, healthcare/medical, and agrochemicals. Chitin and Chitosans in the Bioeconomy covers all major aspects of chitin and chitosan, including structure, biosynthesis, biodegradation, properties of chitin and derivatives, applications, and market. It offers a special focus on the bioeconomy, which is the renewable segment of the circular economy.
• Describes the structure, biosynthesis, and biodegradation of chitin and chitosan
• Covers chitin- and chitosan-based products
• Details valorization of these materials
• Presents information on shell biorefineries
Chitin and Chitosans in the Bioeconomy serves as a reference for polymer scientists and engineers and is also accessible to economists and advanced students.

Table of Contents
1. Introduction. 2. Occurrence of Chitin. 3. Extraction of Chitin and Production of Chitosan. 4. Structure of Chitin and Chitosan. 5. Biosynthesis of Chitin. 6. Biodegradation of Chitin and Chitosan. 7. Properties of Chitin and Chitosan and their Derivatives. 8. Chitin and Chitosan Market and their Applications in the Bioeconomy. 9.
Perspectives of Chitin and Chitosan in the Bioeconomy.