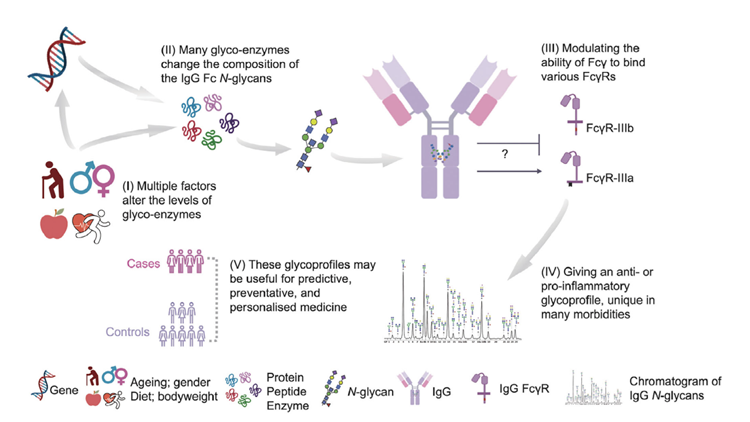
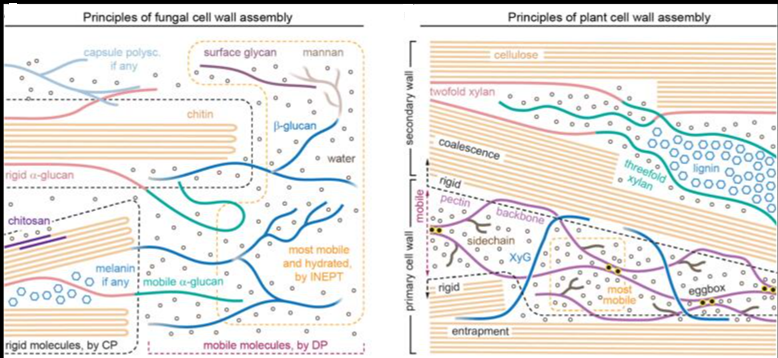
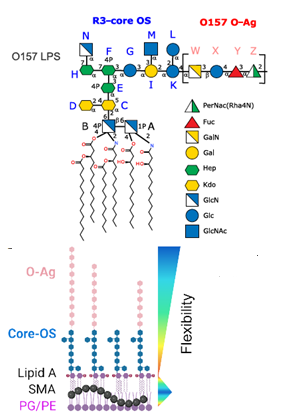
The central dogma of molecular biology traditionally emphasizes nucleic acids and proteins but has often overlooked the vital role of carbohydrates (sugars and glycans) in cellular functions. Carbohydrates form glycoconjugates—such as glycolipids, glycoproteins, and glycoRNAs—by combining with lipids, proteins, and RNA. These structures facilitate signaling, recognition, and dynamic responses within cells. Adopting a glycomics-focused view extends the central dogma by including various biomacromolecular modifications, highlighting glycans as context-dependent molecular signals produced through non-template enzymatic processes. These processes are partly genetically constrained but also structurally unpredictable. Known as the “third alphabet of life,” after nucleic acids and amino acids, the glycan carries extensive information that influences cellular communication, immunity, and disease. Glycoconjugates and newly identified glycoRNAs demonstrate how glycan modifications intersect with nucleic acids. For instance, O-GlcNAcylation in DNA synthesis and DNA damage responses—mediated by enzymes like O-GlcNAc transferase and O-GlcNAcase—affects genome stability and cellular homeostasis. Progress in glycomics, viewed through the lens of the paracentral dogma, uncovers profound insights into glycoconjugates and sugar-encoded information, opening new possibilities for vaccines, targeted therapies, and glycomedicine.