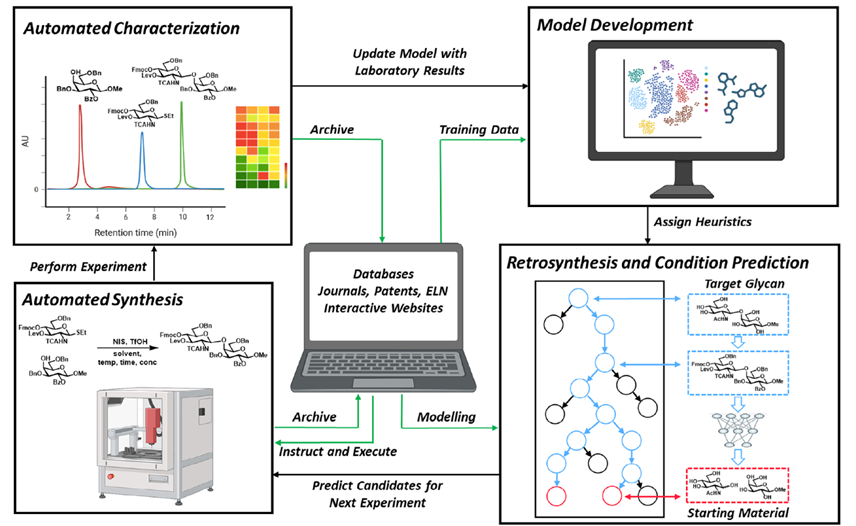
Glycosylation, the key reaction in synthetic glycochemistry, remains entirely unpredictable due to its complex mechanism and the need for protecting groups that impact reaction outcomes. Quick access to defined complex glycans is needed to procure substrates that enable molecular glycobiology. Digital tools can only be employed efficiently when the current experimental practices and reporting are revised. Reporting standards need to be decided upon and then implemented, similar to MIRAGE (Minimum Information Required for A Glycomics Experiment) standards set up by the glycomics community. Big data approaches must include concentration, and glycosylations should be conducted at a well-defined temperature. Along with structured data generation from new experiments and mining the literature, fundamental work concerning reaction order, rate, and activation barriers for glycosylations and auxiliary chemical manipulations is pivotal for designing efficient automated assembly protocols and developing accurate retrosynthetic predictor models.