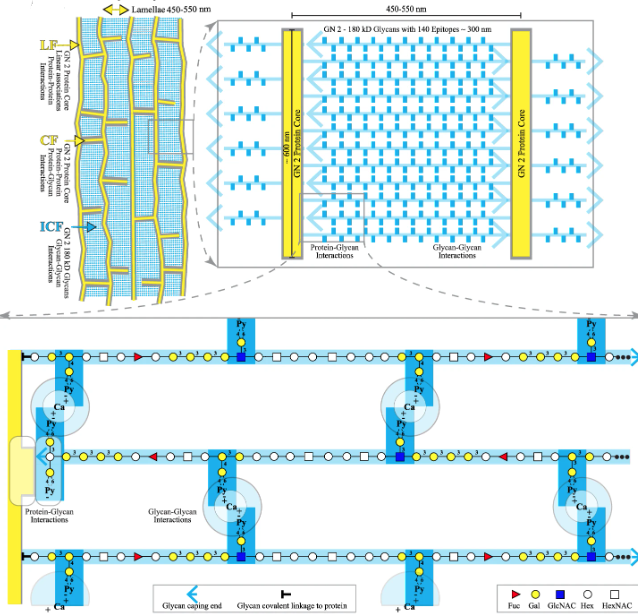
Mucin, proteoglycan, glyconectin, and hyaluronan intermolecular binding in the physiological hydrated state forms the native glycocalyx ultrastructure via the polyvalent interactions of their similar bottle-brush morphologies. This ultrastructure provides a variety of essential cellular recognition adhesion and selective filtration functions. Unfortunately, the glycocalyx architecture was only examined in the non-native dehydrated/fixed state for decades. This has resulted in the visualization of an artefactual unorganized fiber mesh, hindering understanding structure-function relationships. The authors unveil a well-organized glycocalyx lamellar ultrastructure using cryo-SEM after cryo-preservation with minimal sublimation to conserve water and ion distribution and, thereby, native intermolecular interactions. The glycocalyx of human cells and the glyconectin glycocalyx of an evolutionary distant sponge displayed similar self-assembled ultra-structures comprising hierarchical micro- and nanoarrays despite compositional differences. AFM binding strength measurements and cryo-SEM results imply that evolutionarily preserved glycocalyx morphologies are formed by thermodynamically driven self-assembly of glycoconjugates with similar physicochemical properties.