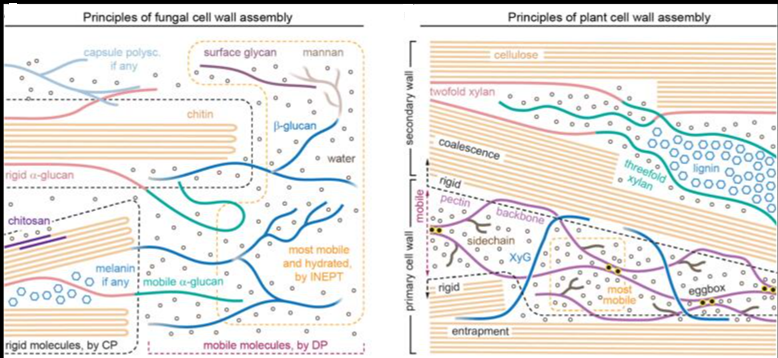
The authors have developed a research strategy, called CryoSeek, to identify uncharacterized bio-entities from natural or endogenous resources using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). They report the discovery of a glycofibril whose primary molecular mass is attributed to a thick glycan backbone. The 3.3 Å resolution cryo-EM reconstruction reveals that the only protein component of the glycofibril, which is approximately 8 nm in diameter, is a linear chain of tetrapeptide repeats. Each tetrapeptide repeat consists of a 3,4-dihydroxyproline (diHyp), a Ser or Thr, and two less conserved residues. Two and one glycan chains are O-linked to the diHyp and Ser/Thr residues, respectively.
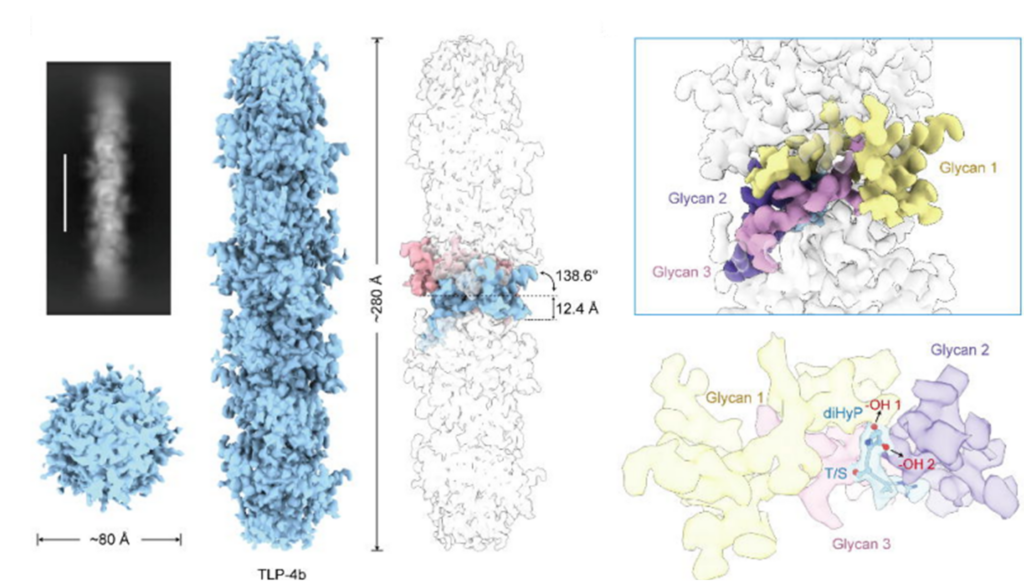
The protein sequence pattern of this glycofibril is similar to that of the recently observed TLP-4, although the glycan chains are different. The authors rename the previously characterized glycofibril as TLP-4a and this one as TLP-4b. The present findings reveal the critical role of glycans in the structural folding of glycoconjugates and shed light on understanding the carbon/nitrogen ratio in biospheres.