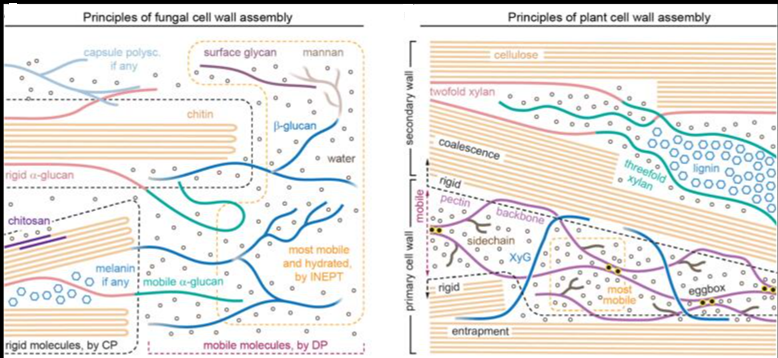
Accurate computational simulations of protein−glycan dynamics are crucial, critically relying on the appropriate parameters, including the water model, because of the extensive hydrogen bonding with glycan hydroxyl groups. A systematic evaluation of water models’ accuracy in simulating protein−glycan interaction at the molecular level is still lacking.
The authors of this study used full atomistic MD simulations and alchemical absolute binding free energy (ABFE) calculations to investigate the performance of five distinct water models in six protein−glycan complex systems. They evaluated water models’ impact on structural dynamics and binding affinity through over 5.8 μs of simulation time per system.
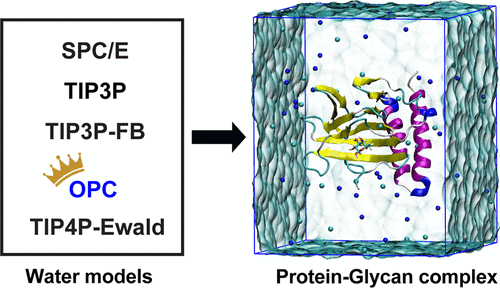
The results reveal that most protein−glycan complexes are stable in the overall structural dynamics regardless of the water model used, while some show noticeable fluctuations with specific water models. More importantly, we discover that the stability of the binding motif’s conformation is dependent on the water model chosen when its residues form weak hydrogen bonds with the glycan. The water model also influences the conformational stability of the glycan in its bound state according to density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Using alchemical ABFE calculations, the authors find that the OPC water model exhibits exceptional consistency with experimental binding affinity data, whereas commonly used models such as TIP3P are less accurate. The findings demonstrate how different water models affect protein−glycan interactions and the accuracy of binding affinity calculations, which is crucial in developing therapeutic strategies targeting these interactions.