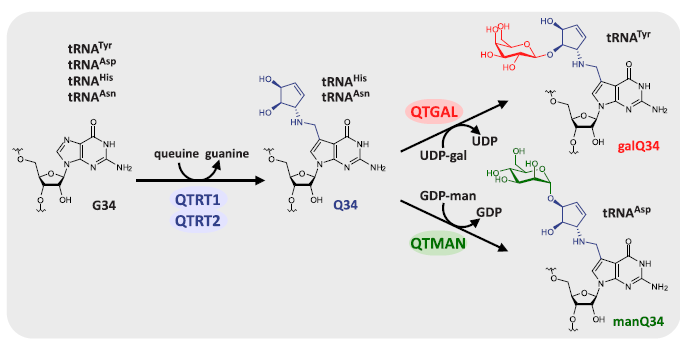
Transfer RNA (tRNA) modifications are critical for protein synthesis. Queuosine (Q), a 7-deaza-guanosine derivative, is present in tRNA anticodons. Q is further glycosylated with galactose and mannose to form galQ and manQ in vertebrate Tyr and Asp tRNAs. However, biogenesis and physiological relevance remain poorly understood. The authors report the biochemical identification of two RNA glycosylases, QTGAL and QTMAN, and the successful reconstitution of tRNA Q-glycosylation with nucleotide diphosphate sugars.
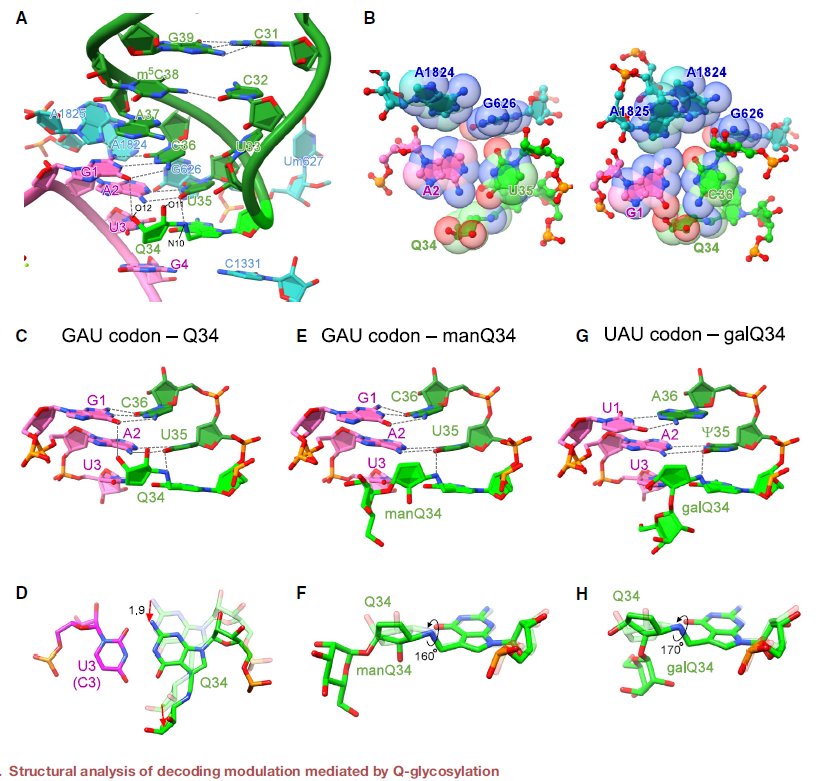
Q-glycosylation slowed elongation at the cognate codons UAC and GAC (GAU), respectively, according to ribosome profiling of knockout cells. The authors found that galactosylation of Q suppressed stop codon read-through. In addition, protein aggregates increased in cells lacking Q-glycosylation, suggesting that Q-glycosylation contributes to proteostasis. Cryo-EM of the human ribosome-tRNA complex revealed the molecular basis of codon recognition regulated by Q-glycosylation.