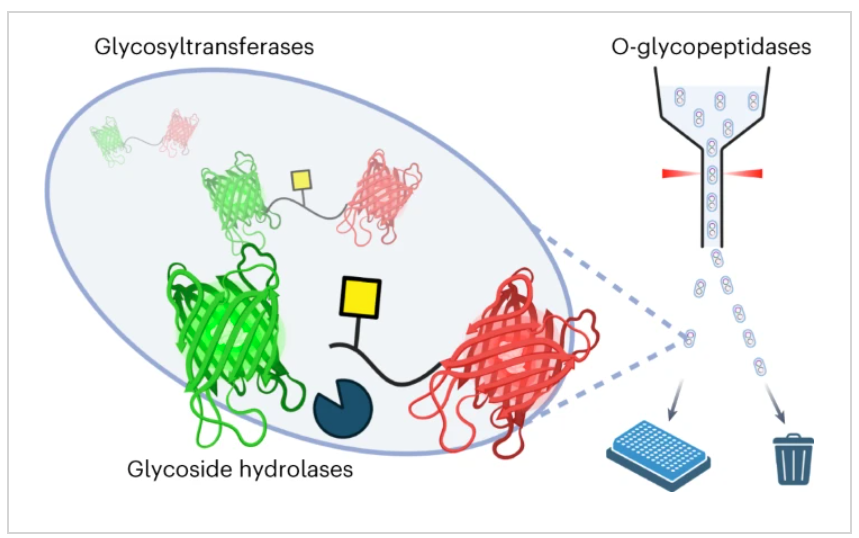
Mucin-type O-glycosylation is a post-translational modification present at the interface between cells, where it has essential roles in cellular communication. However, deciphering the function of O-glycoproteins and O-glycans can be challenging, especially as few enzymes are available for their assembly or selective degradation. Here, to address this deficiency, we developed a genetically encoded screening methodology for the discovery and engineering of the diverse classes of enzymes that act on O-glycoproteins. The method uses { Escherichia col}i engineered to produce an O-glycosylated fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe that can be used to screen for O-glycopeptidase activity. Subsequent cleavage of the substrate by O-glycopeptidases provides a read-out of the glycosylation state of the probe, allowing the method to be used to assay glycosidases and glycosyltransferases. We further show the potential of this methodology in the first ultrahigh-throughput-directed evolution of an O-glycopeptidase.