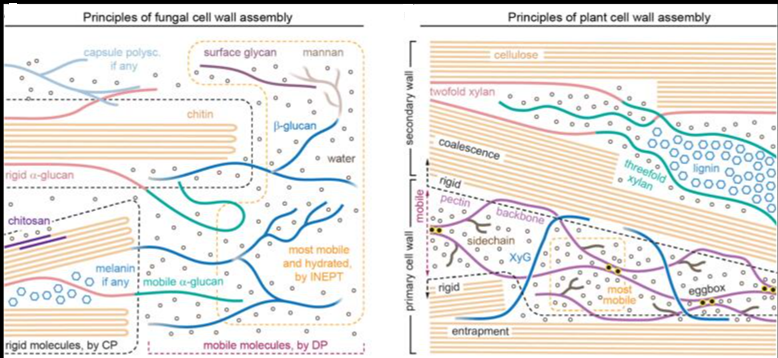
Glycosylation is one of the post-translational modifications, with more than 50% of human proteins being glycosylated. The exact nature and chemical composition of glycans are inaccessible to X-ray or cryo-electron microscopy imaging techniques. Therefore, computational modeling studies and molecular dynamics must be used as a “computational microscope”. The spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2 is heavily glycosylated, and a few glycans play a more functional role “beyond shielding”.
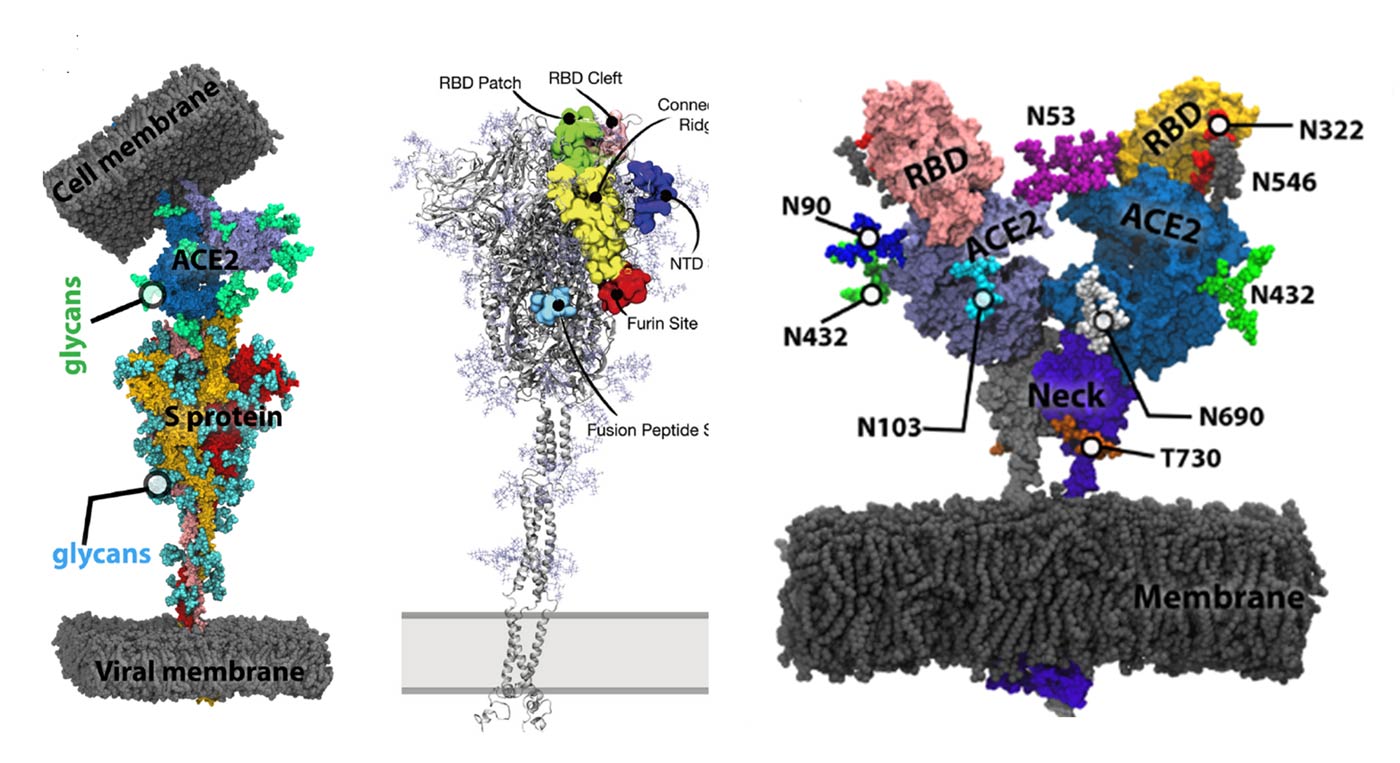
The authors discuss computational investigations of the roles of specific S-protein and ACE2 glycans in the overall ACE2-S protein binding. They highlight different functions of specific glycans demonstrated in myriad computational models and simulations in the context of the SARS-CoV-2 virus binding to the receptor. They discuss interactions between glycocalyx and the S protein, which may be utilized to design prophylactic polysaccharide-based therapeutics targeting the S protein. They underline the recent emergence of coronavirus variants and their impact on the S protein and its glycans.