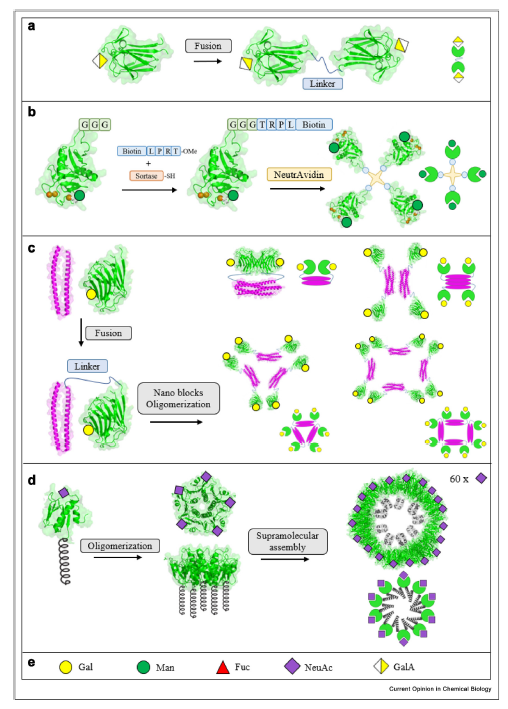
Lectins are non-immunoglobulin and non-catalytic glycan-binding proteins that are able to decipher the structure and function of complex glycans. They are widely used as biomarkers for following the alteration of glycosylation state in many diseases and have applications in therapeutics. Controlling and extending lectin specificity and topology is the key to obtaining better tools. Furthermore, lectins and other glycan-binding
proteins can be combined with additional domains, providing novel functionalities.
The authors provide their views and analyze the current strategy with a focus on synthetic biology approaches yielding novel specificity, but other novel architectures with novel applications in biotechnology or therapy.