Multi-cancer early detection (MCED) is an emerging paradigm to curb cancer mortality by shifting the stage at diagnosis through a single test capturing all cancer types when still confined to their tissue of origin (stage I). Liquid biopsies based on genomic biomarkers could make MCED realistic, but limitations include 10% stage I sensitivity in validation studies; the inability to detect specific types like gliomas; complex assays; and potential overdiagnosis.
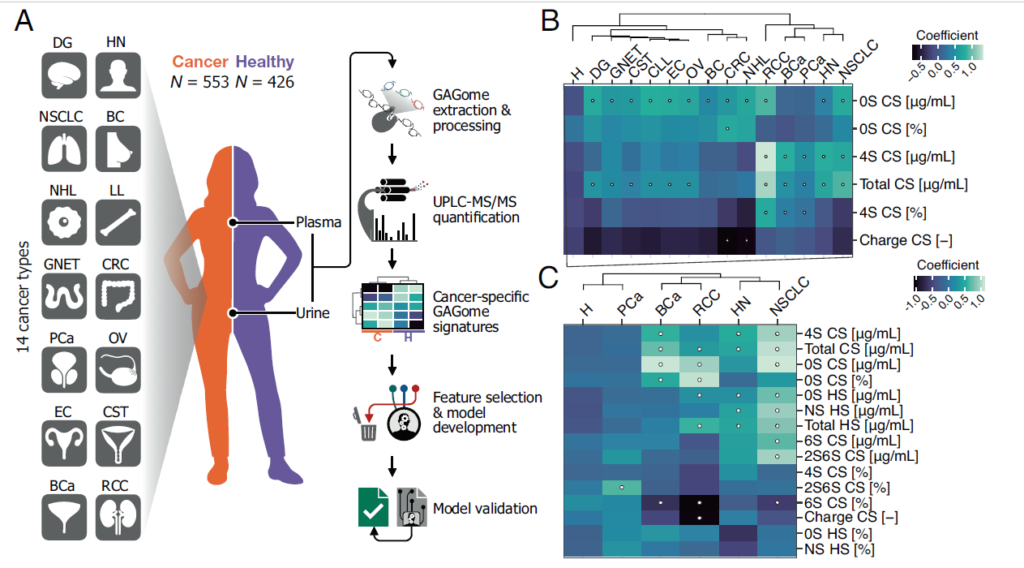
The authors demonstrate the potential of free glycosaminoglycan profiles (GAGomes) as metabolic biomarkers for MCED across 14 cancer types. In a validation study, plasma and urine GAGomes doubled the stage I sensitivity reported by state-of-the-art genomics biomarkers and detected poor prognosis cancers. As such, this simple assay could accelerate MCED implementation.