The ability to reconstitute natural glycosylation pathways or prototype entirely new ones from scratch is hampered by the limited availability of functional glycoenzymes, many of which are membrane proteins that fail to express in heterologous hosts. Here, we describe a strategy for topologically converting membrane-bound glycosyltransferases (GTs) into water-soluble biocatalysts expressed at high levels in the cytoplasm of living cells with retention of biological activity. The authors demonstrate the universality of the approach through the facile production of 98 difficult-to-express GTs, predominantly of human origin, across several commonly used expression platforms.
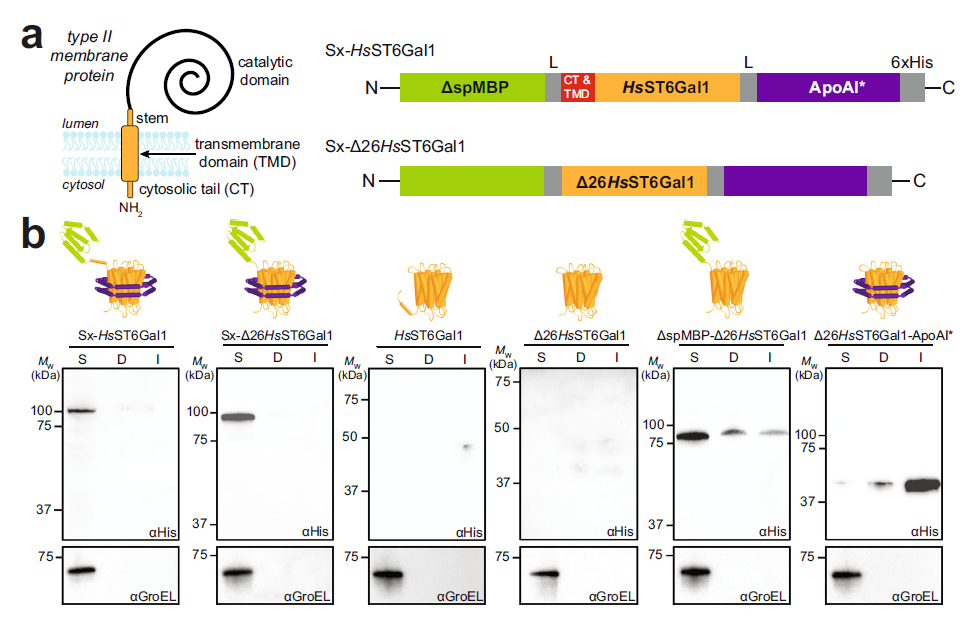
Using a subset of these water-soluble enzymes, the authors perform structural remodeling of free and protein-linked glycans, including those found on the monoclonal antibody therapeutic trastuzumab. Overall, our strategy for rationally redesigning GTs provides a practical and versatile biosynthetic route to large quantities of diverse, enzymatically active GTs, which should find use in structure-function studies as well as in biochemical and biomedical applications involving complex glycomolecules