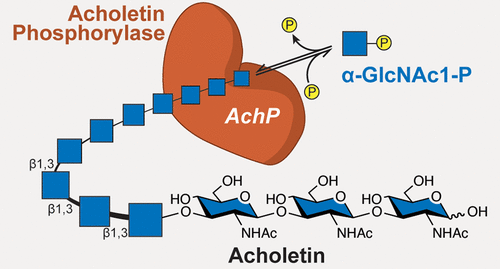
Using genomic data and activity-based screening, the researchers identified a glycoside phosphorylase enzyme from bacteria called Alasmacholep laidlawii.
The authors expressed, purified and crystallized the bacterial enzyme and discovered that it could synthesize a new type of polysaccharide, which they named acholetin. with the Glycoside Phosphorylase being denoted acholetin phosphorylase (AchP)
While the composition of acholetin is similar to chitin, the difference between the glycosidic linkages, 1-3 β- versus 1-4 induces significant 3D differences. Besides, the nature of the way the acholetin chains might interact together remains to be fully characterized to envisage any biotechnological applications. Anyhow, this novel polysaccharide, which could be amenable to chemical modifications similar to those bringing chitin to chitosan, is opening the routes to exciting discoveries and usages.
Credit: Adapted from ACS Central Science 2022, DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c01570