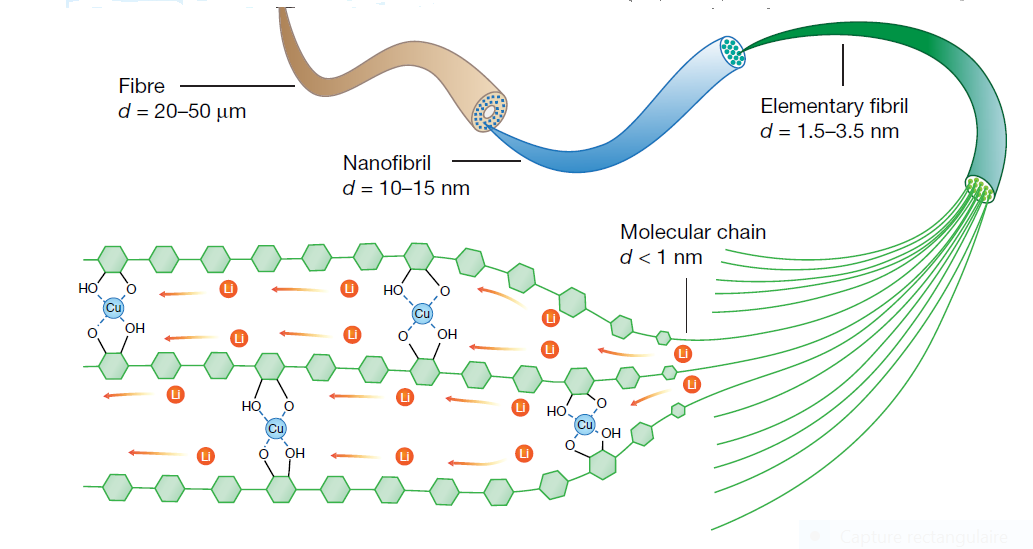
The authors report a general strategy for achieving high-performance solid polymer ion conductors by engineering molecular channels. These molecular channels are provided throughout the coordination of Cu2+ ions with one-dimensional cellulose nanofibrils, which enables the rapid transport of Li+ ions along the polysaccharide chains. This one-dimensional conductor allows ion percolation in thick LiFePO4 solid-state cathodes to be used in batteries with a high energy density. The success of this design strategy creates a class of polymer ion conductors that enable fast conduction by various cations (for example, Na+) with high room-temperature ionic conductivities that have so far been challenging for traditional polymer electrolytes.