Advances in genomics, glycoproteomics and tools from chemical biology have made glycobiology more tractable and understandable. Dysregulated glycosylation plays a major role in disease processes from immune evasion to cognition, sparking research that aims to target glycans for therapeutic benefit. The field is ready for a boom in drug development. Glycobiology has already produced several drugs that have improved human health or are currently being translated to the clinic.
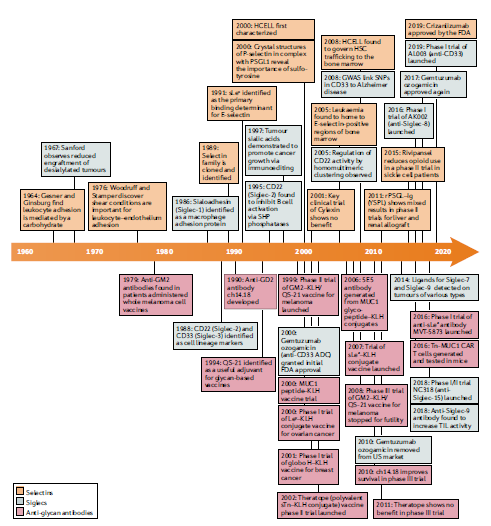
The review by B.A.H. Smith & C.R. Bertozzi, focuses on three areas — selections, Siglecs and glycan- targeted antibodies. It aims to tell the stories behind therapies inspired by glycans and to outline how the lessons learned from these approaches are paving the way for future glycobiology-focused therapeutics. Of significant interest is the timeline of key developments in translational glycobiology, and the recent successes reached over the last decade.
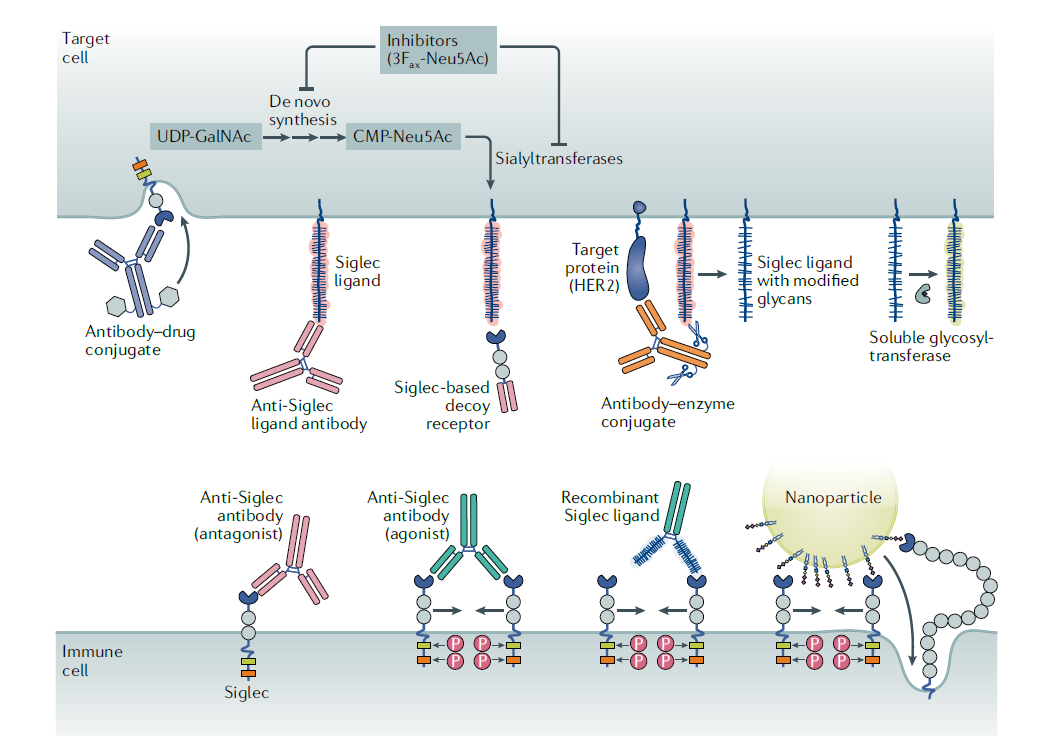
Reference Benjamin A. H. Smith & Carolyn R. Bertozzi,
Nature Reviews | Drug Discovery, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-00093-1