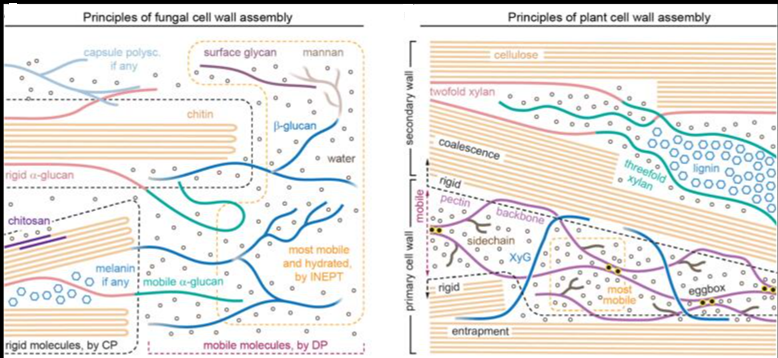
Cellulose is an essential plant cell wall component. Supramolecular plant cellulose synthase complexes organize multiple linear glucose polymers into microfibrils as load-bearing wall components.
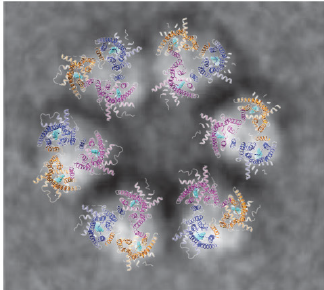
The authors determined the structure of a poplar cellulose synthase CesA homotrimer that suggests a molecular basis for cellulose microfibril formation. This complex, stabilized by cytosolic plant conserved regions and helical exchange within the transmembrane segment, forms three channels occupied by nascent cellulose polymers. Secretion steers the polymers toward a common exit point, which may facilitate protofibril formation. CesAs’ N-terminal domains assemble into a cytosolic stalk that interacts with a microtubule-tethering protein and may thus be involved in CesA localization. These data suggest how cellulose synthase complexes assemble and provide the molecular basis for plant cell wall engineering.