Viral infections kill millions of people and new antivirals are needed. Nontoxic drugs that irreversibly inhibit viruses (virucidal) are postulated to be ideal. Unfortunately, all virucidal molecules described to date are cytotoxic. The cell surface sugars which are responsible for initial viral attachment can be mimicked by antivirals molecules such as heparin or heparin-like molecules.
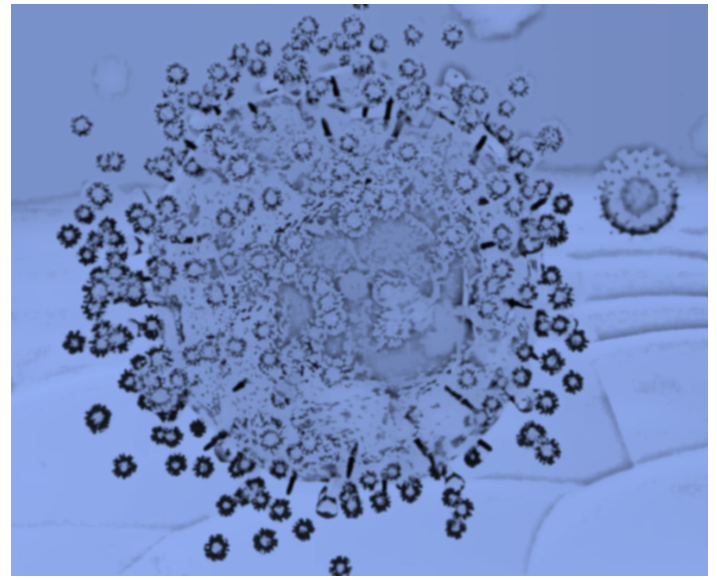
Previous researches explored the potential offered by gold nanoparticles for their multiple viral attachment ligands to create a virucidal drug. Turning their attention to another scaffold, the team of researchers explored the potential of cyclodextrins in their advantages for multivalent presentations. The attachment of mercaptoundecane sulfonic acid to the cyclodextrins resulted in highly efficient virucidal macromolecules. They are broad-spectrum, biocompatible, and virucidal at micromolar concentrations in vitro against many viruses [including herpes simplex virus (HSV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), dengue virus, and Zika virus]. They are effective ex vivo against both laboratory and clinical strains of RSV and HSV-2 in respiratory and vaginal tissue culture models, respectively. Additionally, they are effective when administrated in mice before intravaginal HSV-2 inoculation. Lastly, they pass a mutation resistance test that the currently available anti-HSV drug (acyclovir) fails