Oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) catalyzes the transfer of a high-mannose glycan onto secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Mammals express two distinct OST complexes that act in a cotranslational (OST-A) or post-translational (OST-B) manner. The article reports the high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of human OST-A and OST-B. These structures have similar overall architectures. These structures provide insight into substrate binding of eukaryotic OST complexes and establish that the distinct functions of the two human complexes are based on structural differences of their catalytic subunits STT3A and STT3B.
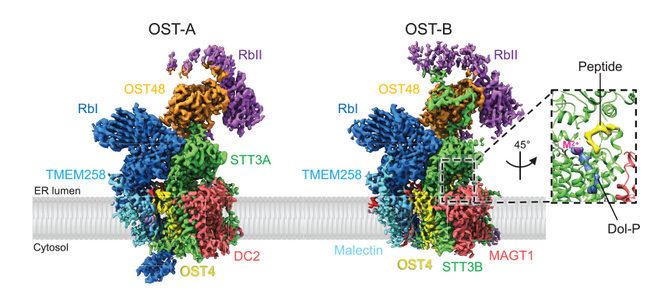
The authors observe an acceptor peptide and dolichol phosphate bound to STT3B, but only dolichol phosphate in STT3A, suggesting distinct affinities of the two OST complexes for protein substrates.