Introduction
Lignin (from the Latin lignum, meaning wood) is a major component of the vascular plant cell walls. Recently, the presence of
Lignin (from the Latin lignum, meaning wood) is a major component of the vascular plant cell walls. Recently, the presence of
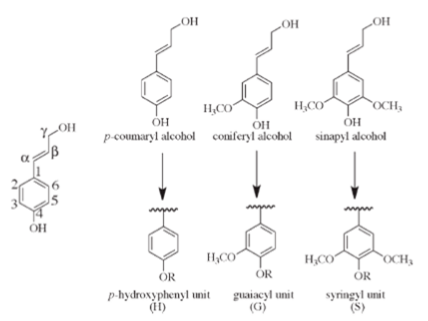
Conventionally, lignin is defined as a polyphenolic polymer basically made from three hydroxycinnamyl alcohols, called the monolignols, respectively, p-coumaryl, coniferyl
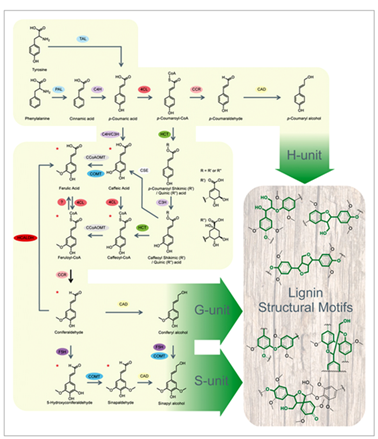
Four steps may be distinguished in lignin formation : 1/ biosynthesis of monolignols ; 2/ transport of monolignols to the plant cell wall ; 3/ enzymatic

The chemical and biological mechanisms leading to lignin assembly in the plant cell wall into a complex 3D structure are
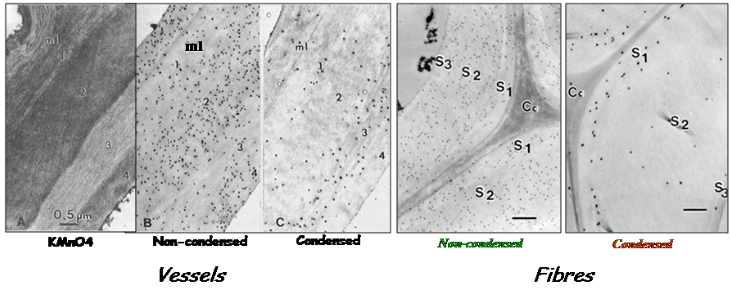
Biochemical studies supported these evidences of spatial heterogeneity of lignin deposition in cell walls associated to tissue maturation Joseleau et al.,
Considering that lignocellulose biomass is one of the most abundant renewable resources, its comprehensive conversion into value-added products, including lignins,
Katia Ruel Katia Ruel is actually retired from her position as Research Director at CNRS (Centre National de la Recherche