Little is known about the biological roles of glycosylated RNAs (glycoRNAs), a recently discovered class of glycosylated molecules, because of a lack of visualization methods. The authors report sialic acid aptamer and RNA in situ hybridization-mediated proximity ligation assay (ARPLA) to visualize glycoRNAs in single cells with high sensitivity and selectivity. The signal output of ARPLA occurs only when dual recognition of a glycan and an RNA triggers in situ ligation, followed by rolling circle amplification of a complementary DNA, which generates a fluorescent signal by binding fluorophore-labeled oligonucleotides.
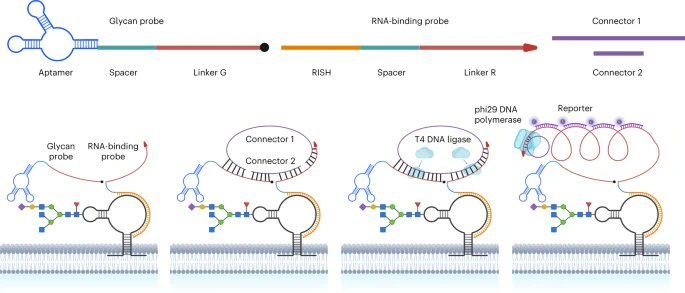
Using ARPLA, the authors detect spatial distributions of glycoRNAs on the cell surface and their colocalization with lipid rafts as well as the intracellular trafficking of glycoRNAs through SNARE protein-mediated secretory exocytosis. Studies in breast cell lines suggest that surface glycoRNA is inversely associated with tumor malignancy and metastasis. Investigation of the relationship between glycoRNAs and monocyte–endothelial cell interactions suggests that glycoRNAs may mediate cell–cell interactions during the immune response.