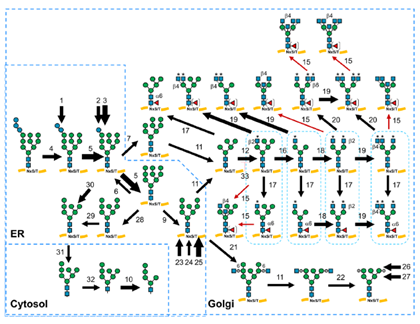
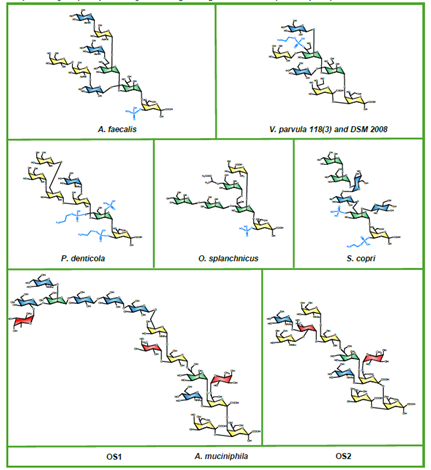
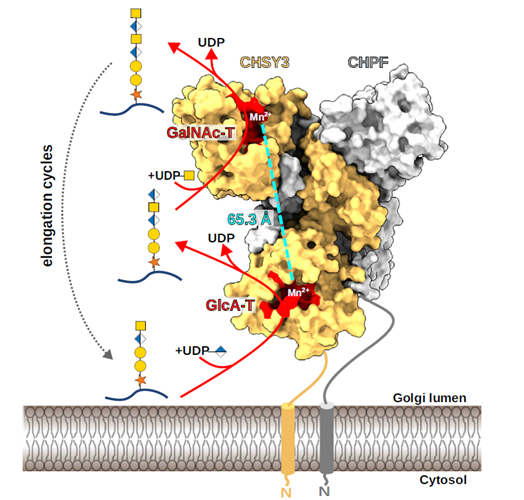
Post-translational modifications such as glycosylation, phosphorylation, and lipidation enhance protein diversity and function. Among these, glycosylation is one of the most prevalent modifications in mammalian cells. The process is tightly regulated at multiple levels, including transcription, translation, protein folding, intracellular transport, localization, and the activities of glycosyltransferases and glycoside hydrolases. It is also affected by the concentration of sugar nucleotides in the Golgi lumen. Unlike nucleic acid and protein synthesis, glycan biosynthesis does not rely on a template, which, combined with the structural complexity of glycans, creates an extremely intricate network. The authors previously developed GlycoMaple, a web-based tool that visualizes and estimates glycosylation pathways from gene expression data. GlycoMaple has been updated to incorporate additional genes and pathways. In this context, we introduce and explore the latest applications and enhancements of GlycoMaple.