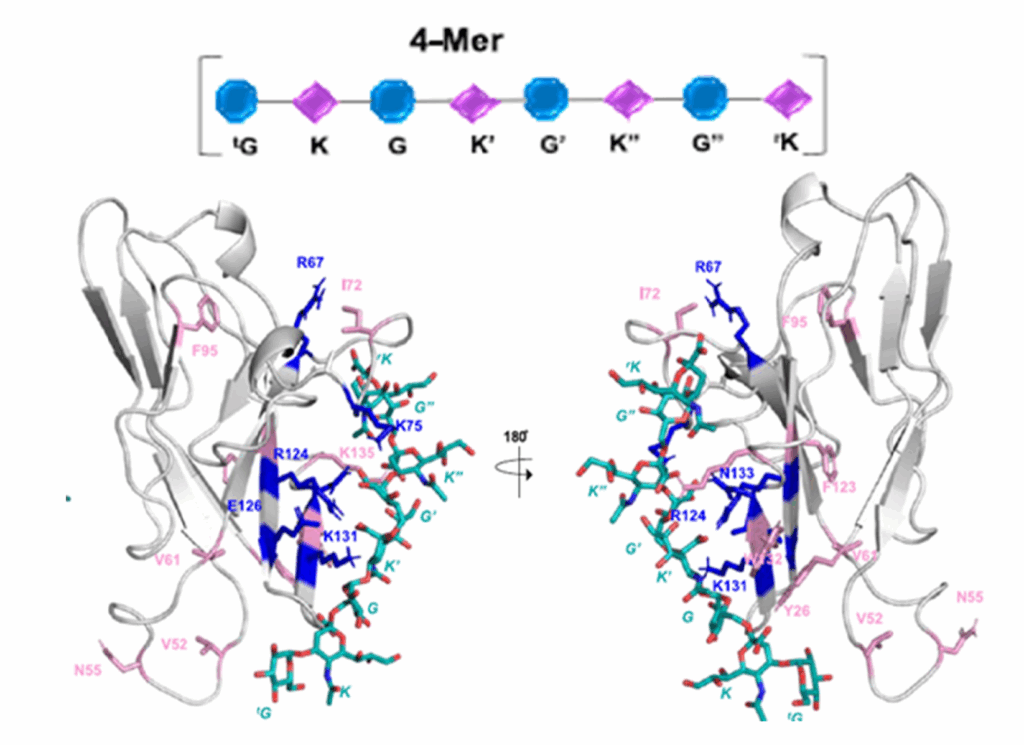
recognize sialic acid residues on cell surfaces. Pathogens and tumor cells exploit Siglecs to evade immune responses and modulate immunity, thereby contributing significantly to the pathogenesis of infectious diseases and cancer. Siglec-7, primarily expressed in natural killer (NK) cells, functions as an inhibitory receptor that tightly regulates immune activity. This study examines the interaction between Siglec-7 and the capsular polysaccharide (CPS) of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup Y (Men-Y), a bacterium whose sialylated CPS is crucial for its virulence. The authors demonstrate that Men-Y CPS binds to inhibitory Siglec-7, potentially dampening immune recognition. They employed a multifaceted approach, combining biochemical and biophysical techniques to dissect this interaction. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and fluorescence titrations were used to quantify the binding specificity and affinity. Ligand- and protein-based nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, combined with computational modeling, provides detailed molecular insights. The authors highlight the critical influence of the Men-Y CPS conformation and sialic acid presentation on Siglec-7 binding. The specific arrangement of α-2,6-linked sialic acids on the CPS is crucial for Siglec-7 binding, demonstrating the importance of the CPS 3D structure. Preliminary immunological assays using stimulated U937 cells (a promonocytic cell line) further support the immunomodulatory role of Siglec-7 mediated by Men-Y CPS. These results offer valuable insights into the development of targeted therapeutic strategies against bacterial infections