Fares, M., Imberty, A. & Titz, A
Bacteria often utilize their lectins to promote pathogenesis. With the rise in anti-microbial resistance (AMR), targeting lectins with inhibitors presents a promising opportunity to enhance the host’s ability to clear the pathogen.
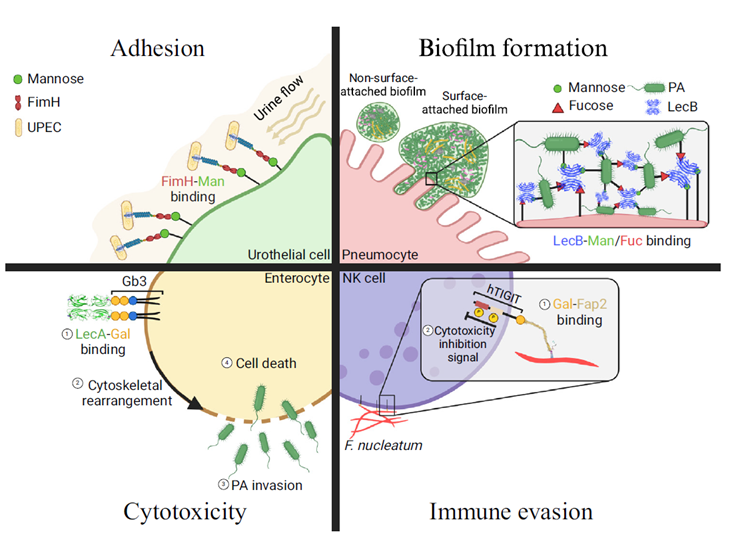
Ongoing research continues to reveal a growing range of functions for bacterial lectins in pathogenesis, including host recognition and adhesion, biofilm formation, cytotoxicity, and immune evasion, with individual lectins often playing multiple roles in these processes.
Recent advances in targeting lectins with glycomimetics and vaccination have yielded early clinical success, consolidating their potential as therapeutic targets.
Underexplored and novel lectins present a gap in the literature, with their biological functions still poorly understood.