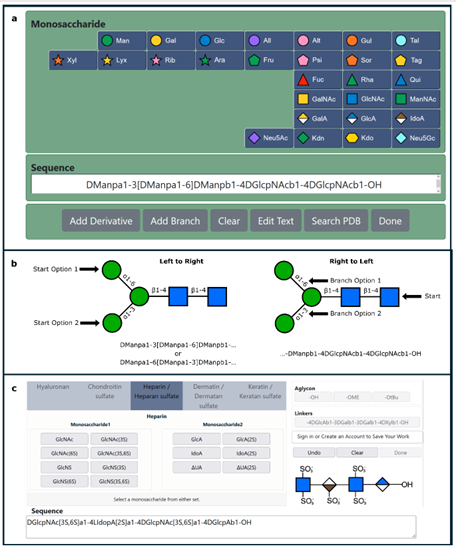
Amylose, a linear polymer comprised of α-1,4-linked glucopyranose units, is renowned for its propensity to crystallize into a parallel double helix structure. However, direct evidence of this duplex formation in solution has remained elusive for decades. The article presents a novel approach to detect the dimerization of short amylose chains in solution using NMR spectroscopy. By labeling the glucans at the reducing-end with an aromatic moiety, the authors overcome chemical shift degeneracy, resulting in distinct signals for both single-stranded and duplex amylose configurations.
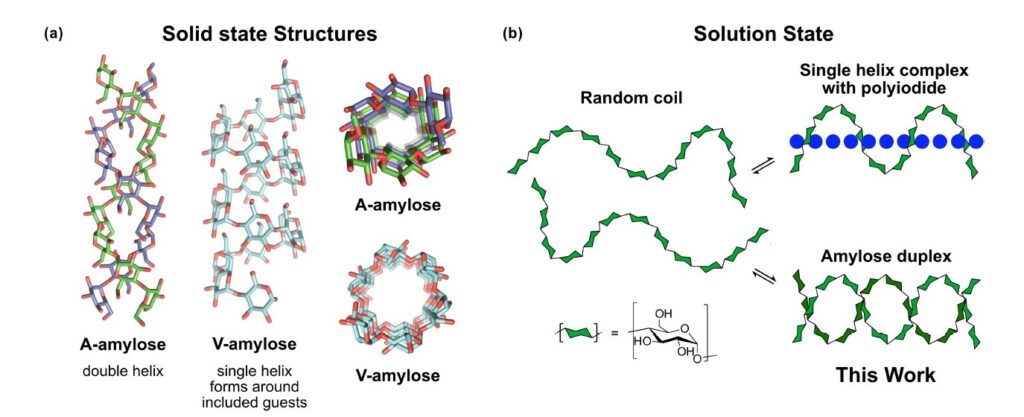
To facilitate this investigation, the authors synthesized a series of α-1,4 glucans with varying lengths containing 6, 12, 18, and 22 glucose units, each labelled with 4-aminobenzamide. This comprehensive setup enabled the first systematic thermodynamic analysis of amylose association in solution. The findings reveal that the dimerization process is enthalpically driven but entropically unfavourable. Additionally, they observed that beyond a critical length of 12 glucose residues, each additional pair of glucose units contributes to a stabilization of the duplex structure by approximately 0.85 kJ/mol.
This fundamental understanding of amylose dimerization serves as a cornerstone for quantitatively elucidating starch structure, gelation phenomena, and enzymatic digestion processes. Moreover, this research lays the groundwork for leveraging α-1,4-glucans in the strategic design and development of self-assembled materials with tailored properties and functionalities.