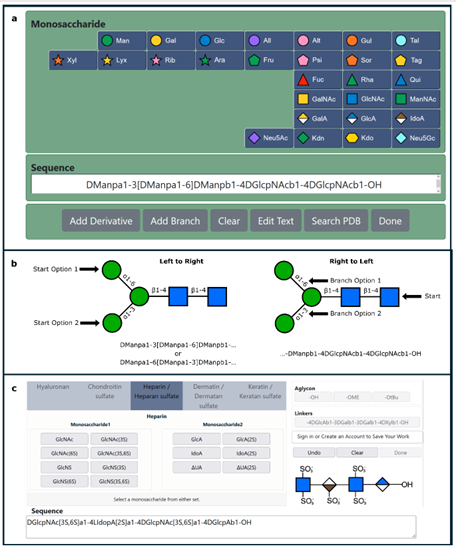
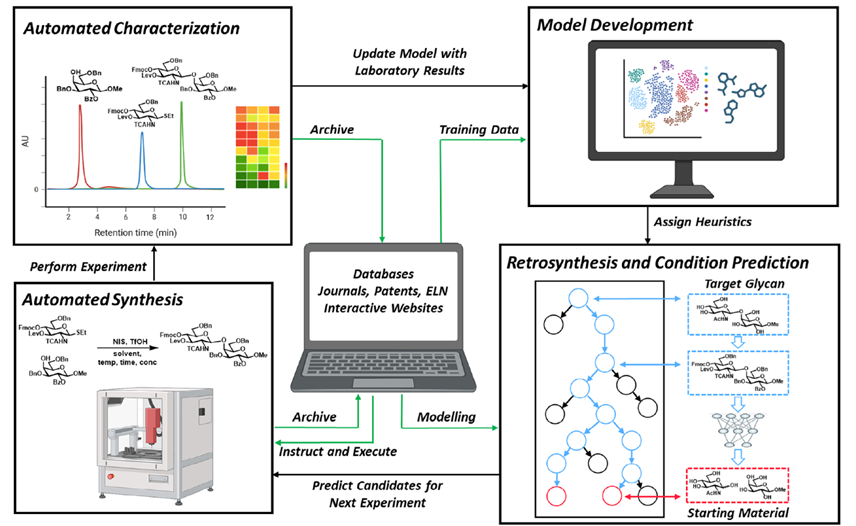
Assessing Genetic Algorithm-Based Docking Protocols
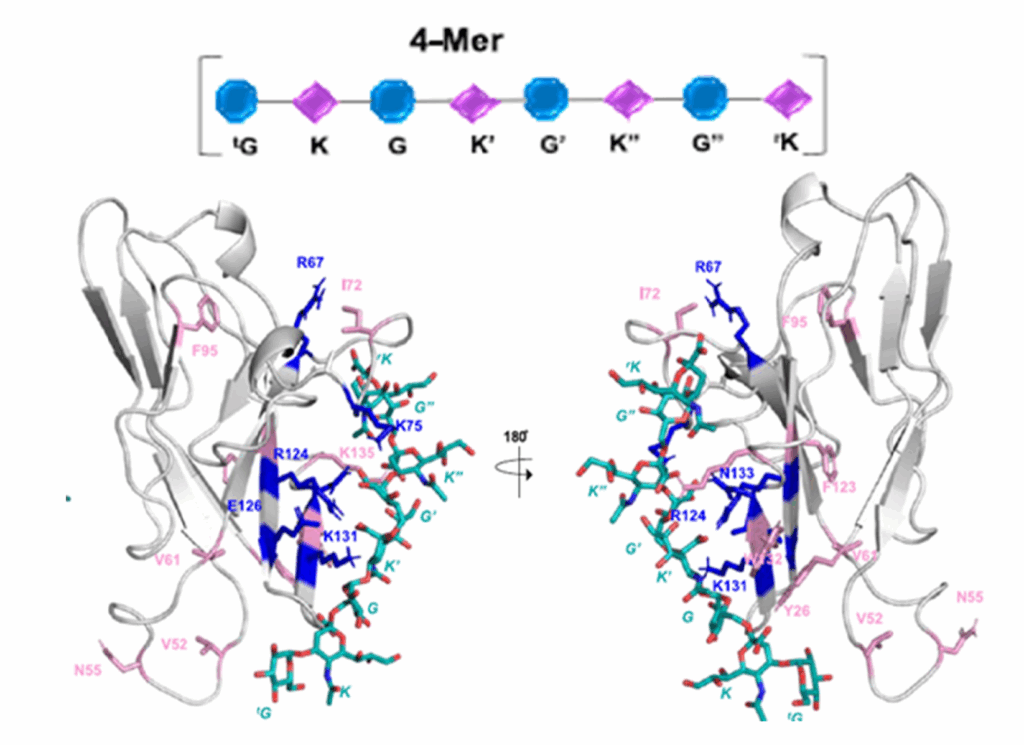
Although molecular docking has evolved dramatically over the years, its application to glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) has remained challenging because of their intrinsic flexibility, highly anionic character and somewhat ill-defined binding site on proteins. GAGs have been treated as either fully “rigid” or fully “flexible” in molecular docking. The authors reasoned that an intermediate semirigid docking (SRD) protocol might better recapitulate native heparin/heparan sulfate (Hp/HS) topologies. They investigate 18 Hp/HS–protein co-complexes containing chains from disaccharide to decasaccharide using genetic algorithm-based docking with rigid, semi-rigid, and flexible docking protocols.

Their work reveals that rigid and semi-rigid protocols recapitulate native poses for longer chains (5 to10 mers) significantly better than the flexible protocol, while 2 to 4-mer poses are better predicted using the semi-rigid approach. More importantly, the semi-rigid docking protocol will likely perform better when no crystal structure information is available. They present a new parameter for parsing selective versus non-selective GAG–protein systems, which relies on two computational parameters: consistency of binding (i.e., RMSD) and docking score (i.e., GOLD Score). The new semi-rigid protocol, combined with the new computational parameter, is expected to be particularly useful in high-throughput screening of GAG sequences for identifying promising druggable targets and drug-like Hp/HS sequences.