Methods for direct covalent ligation of microorganism surfaces remain poorly reported and primarily based on metabolic engineering for bacteria and cell functionalization. While effective, a faster method avoiding the bio-incorporation step would be highly complementary. The authors used N- N-methyl luminol (NML), a fully tyrosine-selective protein anchoring group after one-electron oxidation, to label the surface of viruses, living bacteria and cells. The functionalization was performed electrochemically and in situ by applying an electric potential to aqueous buffered solutions of tagged NML containing the viruses, bacteria or cells.
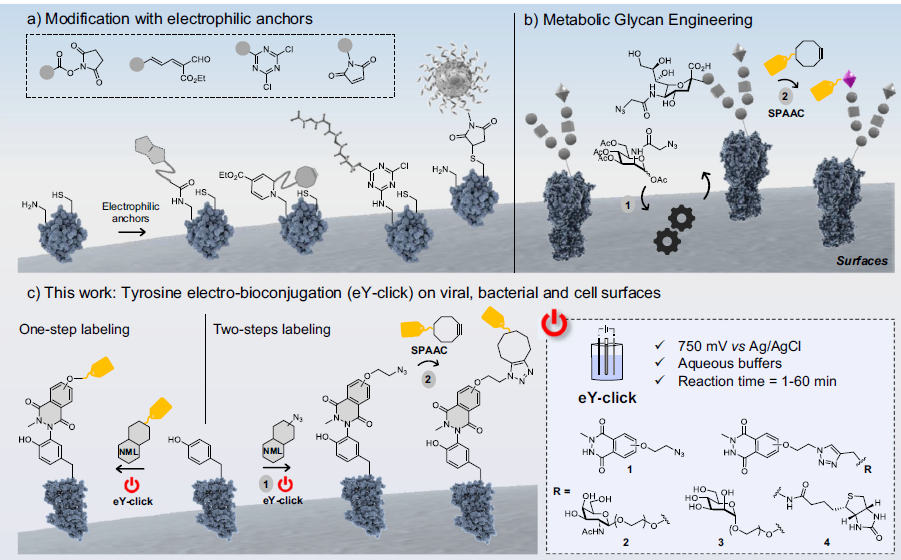
The broad applicability of the click-electrochemistry method was explored on recombinant adeno-associated viruses (rAAV2), Escherichia coli (Gram-) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (Gram + ) bacterial strains, and HEK293 and HeLa eukaryotic cell lines. Surface electro-conjugation was achieved in minutes to yield functionalized rAAV2 that conserved structural integrity and infectivity properties and living bacteria and cell lines that were still alive and could divide.