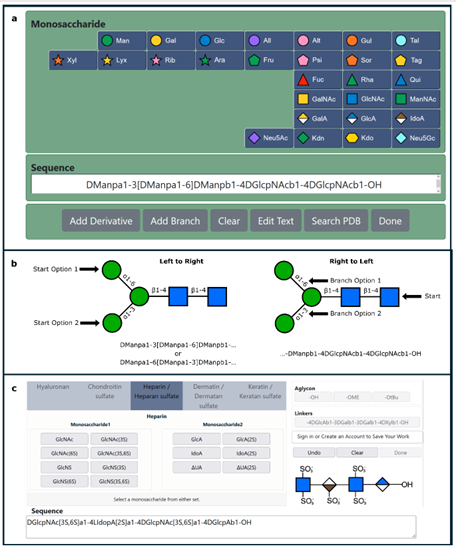
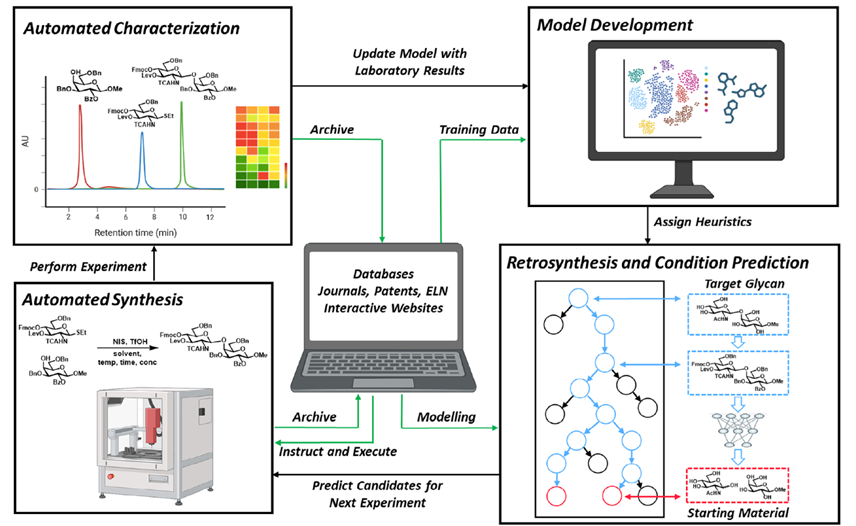
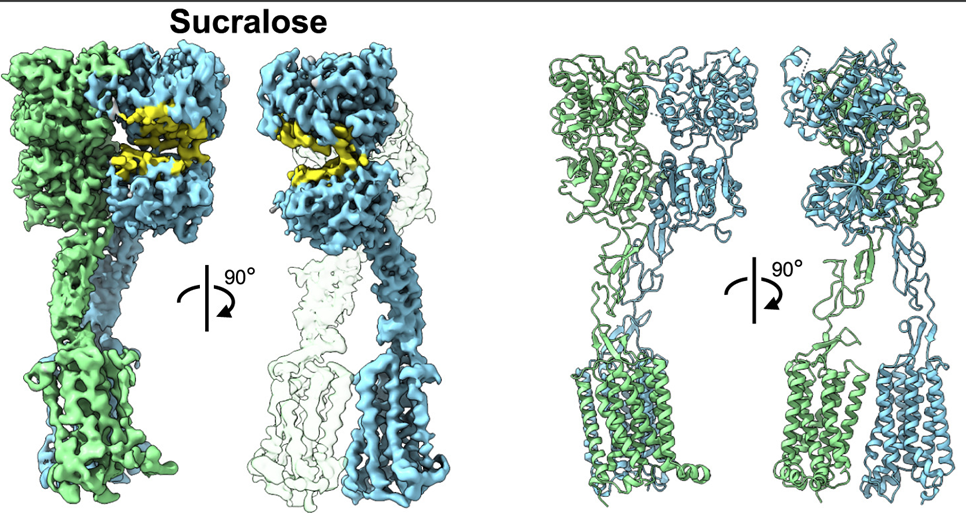
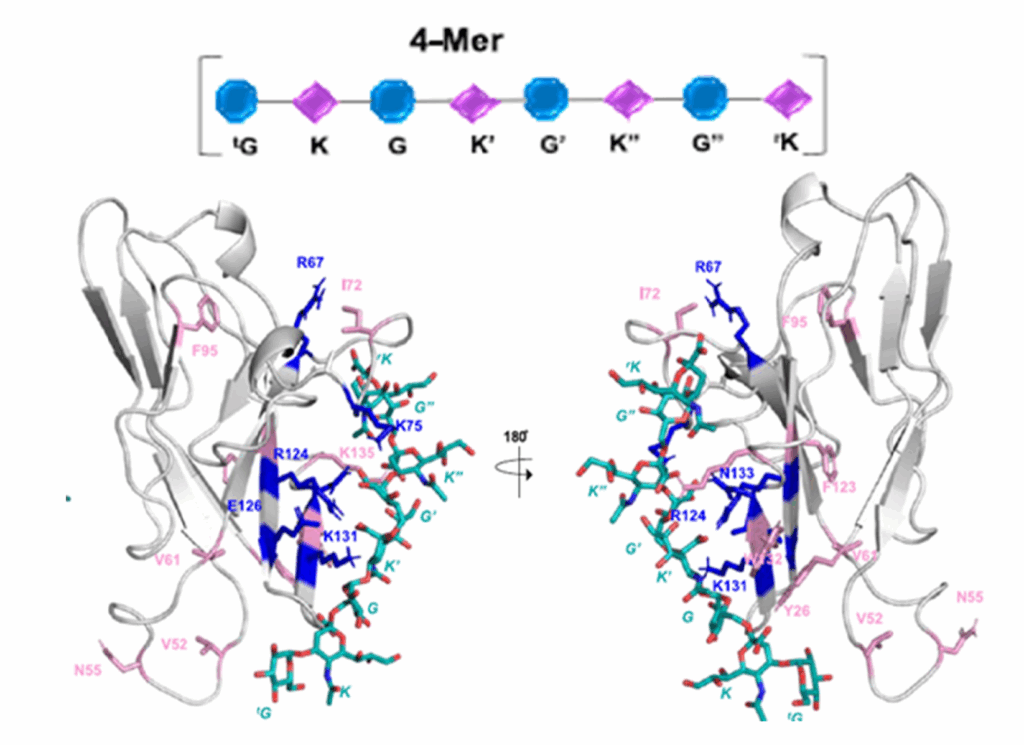
Biosensing or diagnostic applications that use glycan sequences as targets are limited by the cross-reactivity of glycans. The authors introduce a library of synthetic analogues of a single glycan ligand as a powerful approach to obtaining fingerprint binding profiles since the binding sites of different proteins that all recognize a given glycan will not be identical.
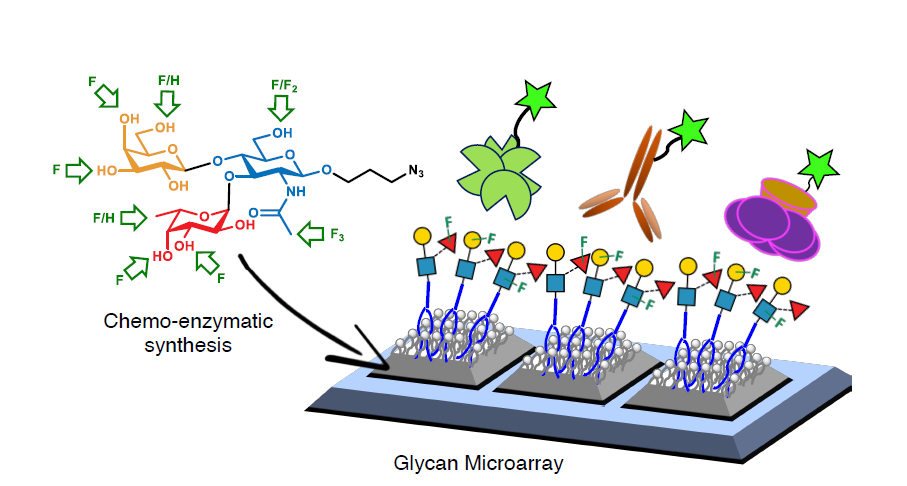
The article reports the enzymatic synthesis of a 150-member library of fluorinated Lewisx analogs (“glycofluoroforms”) using naturally occurring enzymes and fluorinated monosaccharide building blocks and the incorporation of a subset into lipid-bound glycan probes or into glyconanoparticles to probe protein binding in both high-throughput glycan microarray screening analyses and solution-based nanoparticle interaction studies. These fluorinated Lewisx analogues, which NMR studies showed to have very similar 3D structures to those of nonfluorinated Lewisx, showed varying degrees of increased or decreased binding to a range of proteins. Different proteins have different preferences and tolerances for binding.