Despite decades of research, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) have not been known to interact with sialyl transferases (STs). Using an in-house combinatorial virtual library screening (CVLS) technology, the authors investigated seven human isoforms, including ST6GAL1, ST6GAL2, ST3GAL1, ST3GAL3, ST3GAL4, ST3GAL5, and ST3GAL6, and predicted that GAGs, especially heparan sulfate (HS), are likely to differentially bind to STs.
Exhaustive CVLS and molecular dynamics studies suggested that the common hexasaccharide sequence of HS preferentially recognized ST6GAL1 in a site overlapping the binding site of the donor substrate CMP-Sia. Interestingly, CVLS did not ascribe any special role to the rare 3-O-sulfate modification of HS in ST6GAL1 recognition. The computational predictions were tested using spectrofluorimetric studies, which confirmed preferential recognition of HS over other GAGs. A classic chain length-dependent binding of GAGs to ST6GAL1 was observed with polymeric HS displaying a tight affinity of ∼65 nM. Biophysical studies also confirmed a direct competition between CMP-Sia and an HS oligosaccharide and CS polysaccharide for binding to ST6GAL1.
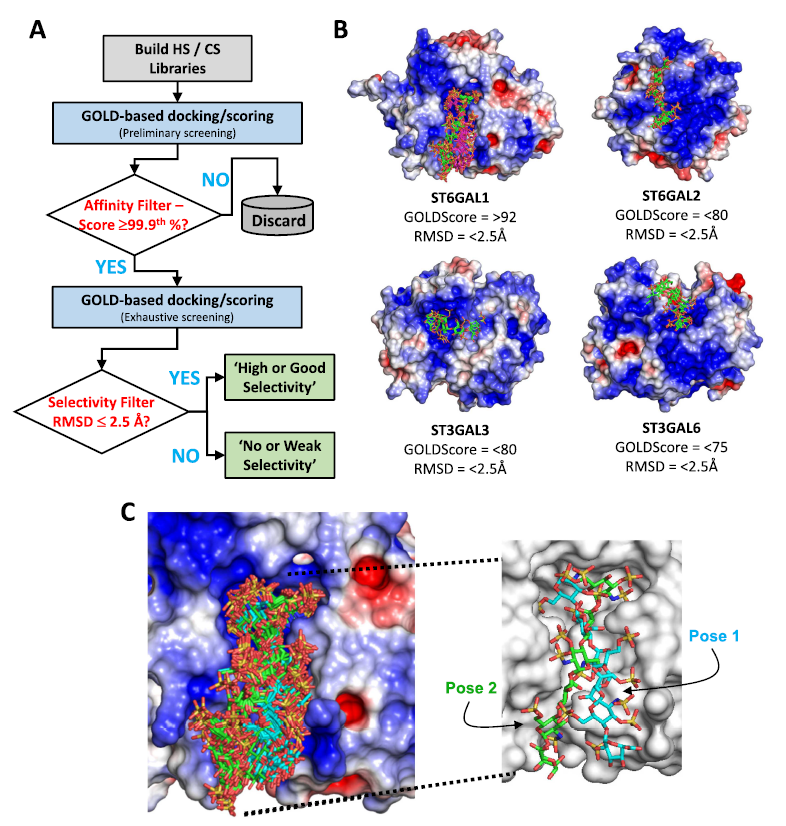
Overall, the novel observation that GAGs bind to ST6GAL1 with high affinity and compete with the donor substrate is likely to be important because modulation of sialylation of glycan substrates on cells has considerable physiological/pathological consequences. The work brings forth the possibility of developing GAG-based chemical probes of ST6GAL1.