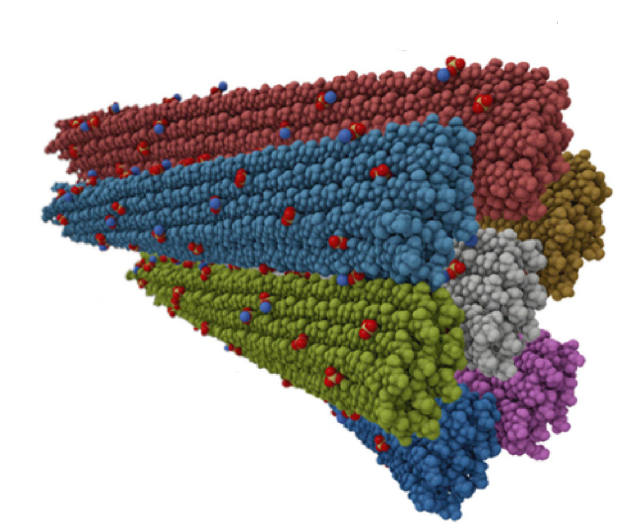
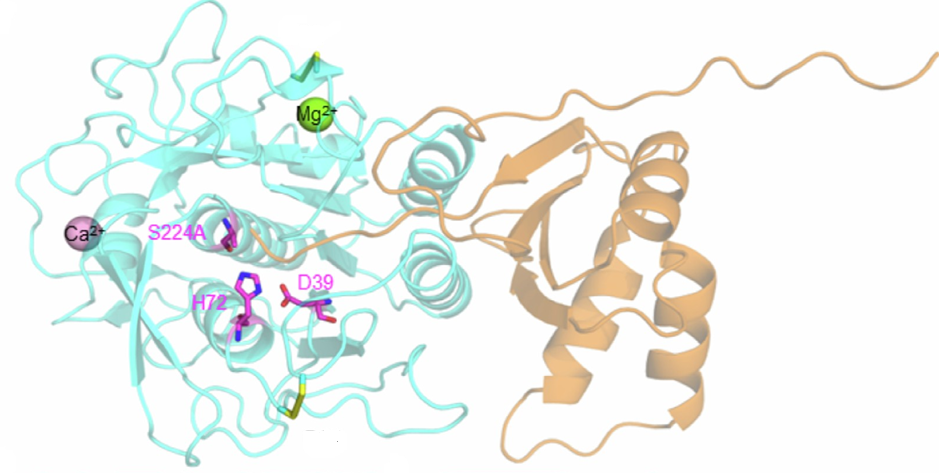
The trimeric spike (S) glycoprotein of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) is responsible for virus-host recognition and membrane fusion; it is the main target for vaccine development and antigenic analysis. The two strains’ atomic structures of the recombinant PEDV S proteins have been reported, but they reveal distinct N-terminal domain 0 (D0) architectures that may correspond to different functional states. The existence of the D0 is a unique feature of alphacoronavirus.
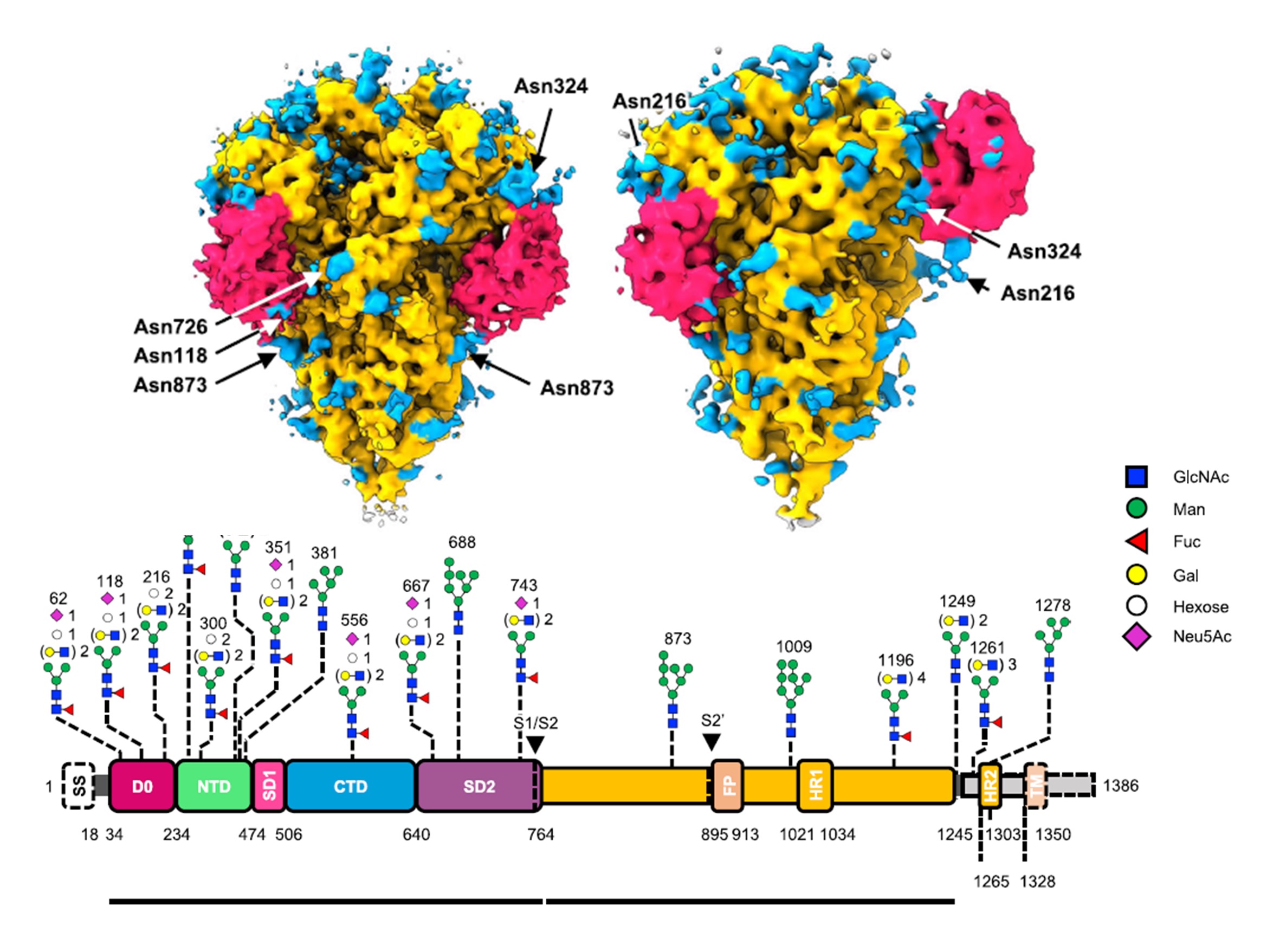
A combined cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis establishes, in situ, the asynchronous S protein motions on intact viral particles of a highly virulent PEDV Pintung 52 strain. The cryo-EM-solved structure of the recombinant S protein derived from a porcine cell line reveals additional domain motions likely associated with receptor binding. The integration of mass spectrometry and cryo-EM, data delineates the complex compositions and spatial distribution of the PEDV S protein N-glycans. It demonstrates the functional role of a key N-glycan in modulating the D0 conformation.