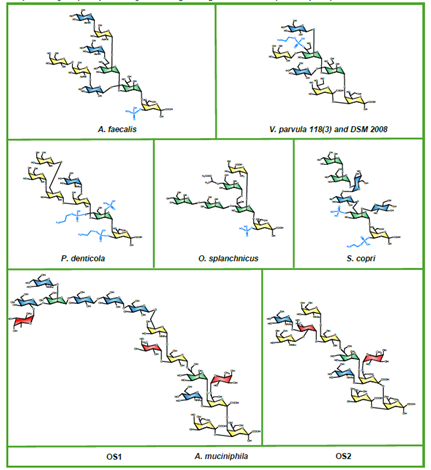
Shigella, the causative agent of shigellosis, is among the leading causes of diarrheal diseases with high morbidity in low-income countries. Relying on chemical synthesis, the design of a multidisciplinary strategy yielded an original glycoconjugate vaccine candidate (SF2a-TT15) targeting Shigella flexneri 2a (SF2a). SF2a-TT15 contains synthetic 15mer oligosaccharides. They correspond to three non-Oacetylated repeats, linked at its reducing end to tetanus toxoid through a thiol-maleimide spacer. The scale-up feasibility under GMP conditions of a high yielding bioconjugation process established a reproducible and controllable glycan/protein ratio.
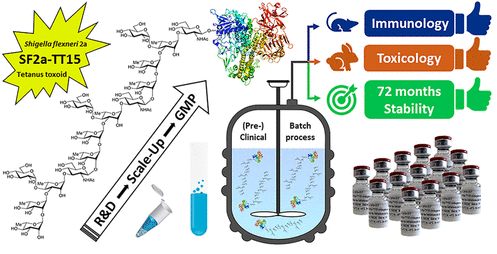
Preclinical and clinical batches were conducted following specifications from ICH guidelines and WHO recommendations for polysaccharide conjugate vaccines. The SF2a-TT15 vaccine candidate passed all toxicity-related criteria. It was immunogenic in rabbits and elicited bactericidal antibodies in mice. The induced IgG antibodies recognized a large panel of SF2a circulating strains. These preclinical data pave the way for the first-in-human study for SF2a-TT15, demonstrating safety and immunogenicity. This contribution discloses the yet unreported feasibility of the GMP synthesis of conjugate vaccines featuring a unique homogeneous synthetic glycan hapten fine-tuned to protect against infectious disease.