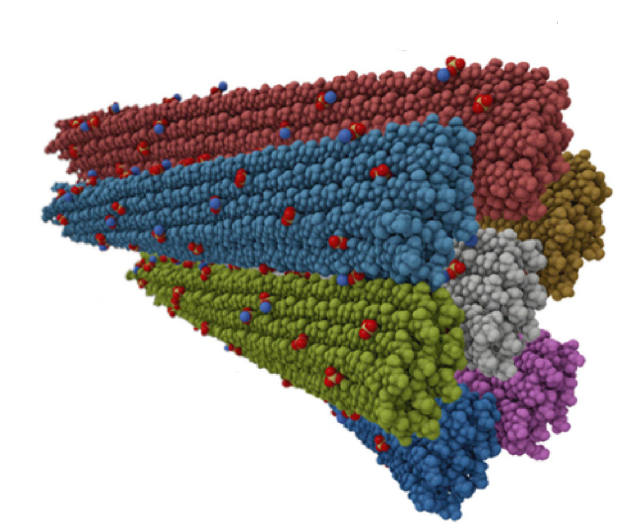
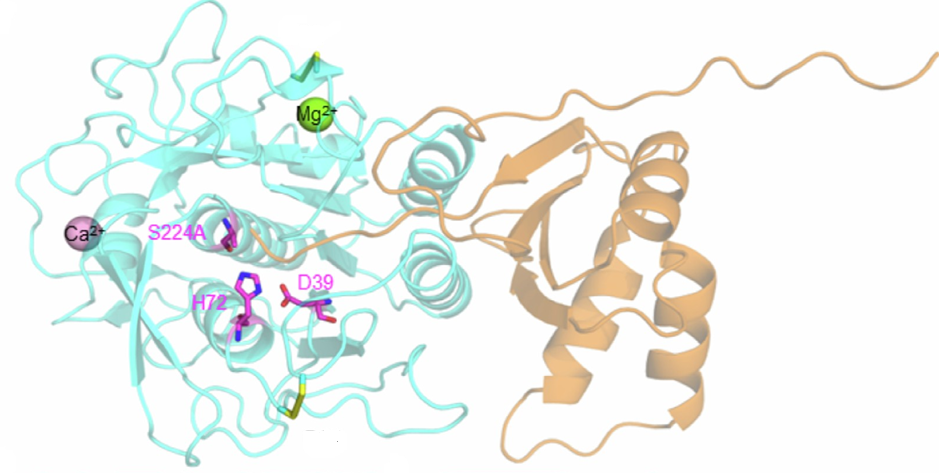
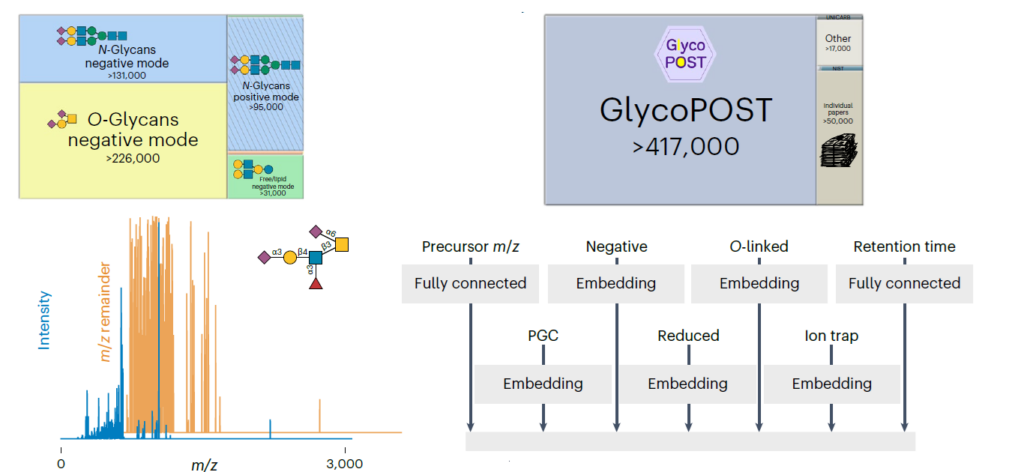
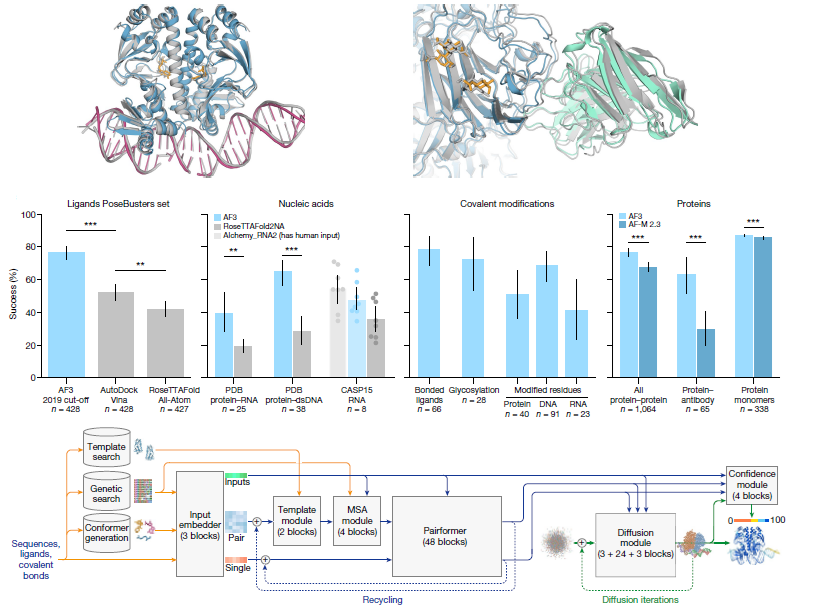
The complex glycans comprising ‘dietary fibre’ evade the limited repertoire of human digestive enzymes. They feed the vast community of microbes in the lower gastrointestinal tract. As such, complex glycans drive the composition of the human gut microbiota (HGM) and, in turn, influence diverse facets of our nutrition and health. To access these otherwise recalcitrant carbohydrates, gut bacteria produce coordinated, substrate-specific arsenals of carbohydrate-active enzymes, glycan-binding proteins, oligosaccharide transporters, and transcriptional regulators. A recent explosion of biochemical and enzymological studies of these systems has led to the discovery of manifold new carbohydrate-active enzyme (CAZyme) families. Crucially underpinned by structural biology, these studies have also provided unprecedented molecular insight into the exquisite specificity of glycan recognition in the diverse CAZymes and non-catalytic proteins from the HGM. The revelation of a multitude of new three-dimensional structures and substrate complexes constitutes a ‘gold rush’ in the structural biology of the human gut microbiota.