Chloroplast membranes have a high content of the uncharged galactolipids monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) and digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG). These galactolipids are essential for the biogenesis of plastids and functioning of the photosynthetic machinery. A monotopic glycosyltransferase, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase synthesizes the bulk of MGDG. It is embedded in the outer leaflet of the inner envelope membrane of chloroplasts. The protein transfers a galactose residue from UDP-galactose to diacylglycerol (DAG); it needs anionic lipids such as phosphatidylglycerol (PG) to be active.
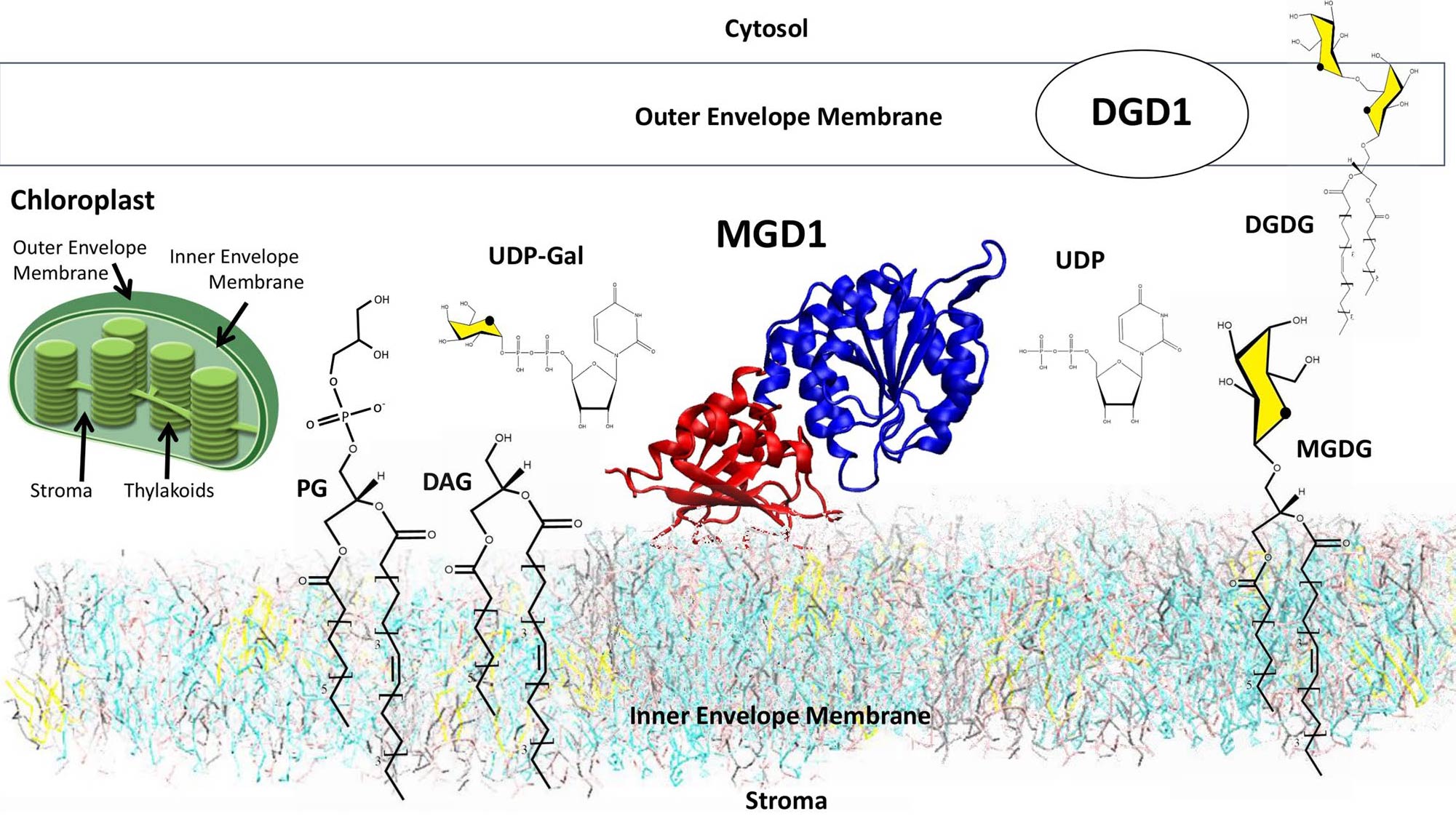
The intricacy of the organization and the process of active complex assembly and synthesis have been investigated at the Coarse-Grained and All-Atom of computer simulation levels to cover large spatial and temporal scales. The following self-assembly process and catalytic events can be drawn; (1) in the membrane, in the absence of protein, there is a spontaneous formation of PG clusters to which DAG molecules associate, (2) a reorganization of the clusters occurs in the vicinity of the protein once inserted in the membrane, (3) an accompanying motion of the catalytic domain of the protein brings DAG in the proper position for the formation of the active complex MGD1/UDP-Gal/DAG/PG for which an atomistic model of interaction is proposed.