Core-fucosylation is an essential biological modification by which fucose is transferred from GDP-β-L-fucose to the innermost N-acetylglucosamine residue of N-linked glycans. A single human enzyme α1,6-fucosyltransferase (FUT8) is the only enzyme responsible for this modification via the addition of α-1,6-linked fucose to N-glycans.
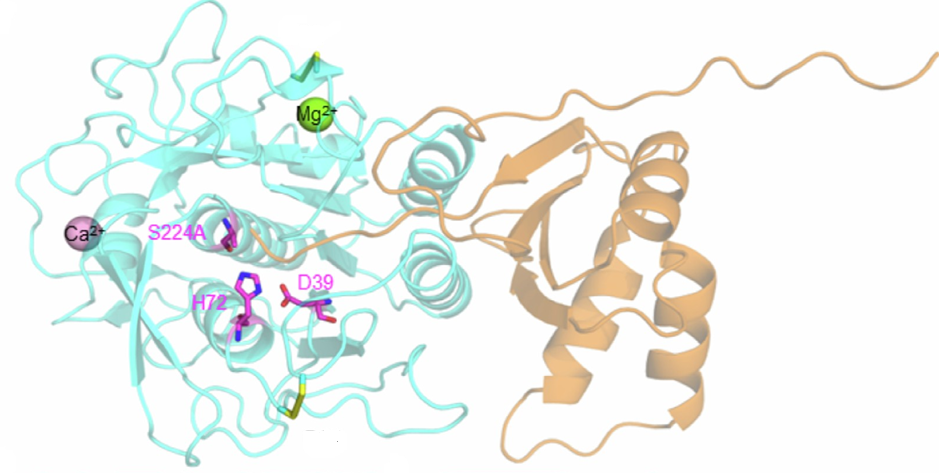
To date, the details of substrate recognition and catalysis by FUT8 remain unknown. THe article reports the crystal structure of FUT8 complexed with GDP and a biantennary complex N-glycan. The quality of the resolution of the three-dimensional structure (PDB with accession code 6TKV) offers highly detailed insights into both substrate recognition and catalysis.
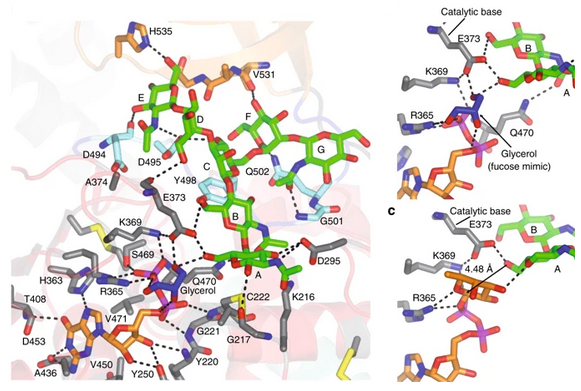
FUT8 follows an SN2 mechanism and deploys a series of loops and an α-helix which all contribute in forming the binding site. An exo-site, formed by one of these loops and an SH3 domain, is responsible for the recognition of branched sugars, making contacts specifically to the α1,3 arm GlcNAc, a feature required for catalysis.
PS. At the time the article was published on 20-02_2020 an article entitled “Structural basis of substrate recognition and catalysis by fucosyltransferase 8” co-authored by M.A. Järvå, M. Dramicanin, J.P. Lingford, R. Mao, A. John, K. Jarman, R.W. Grinter & E.D. Goddard-Borger appeared as a bioRxix preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.14.949818.